版本 9587a39e55ea1a23109cc360aef4b6bd2288b666
Changes from 9587a39e55ea1a23109cc360aef4b6bd2288b666 to current
---
title: Git
categories: 版本控制
...
簡介
====
關於 git 的簡介可參考 Wikipedia: `Git<http://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/Git>`_
關於 git 的簡介可參考 Wikipedia: [Git](http://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/Git)
檔案在git的旅程
--------------
.. image:: /git_file_status.PNG
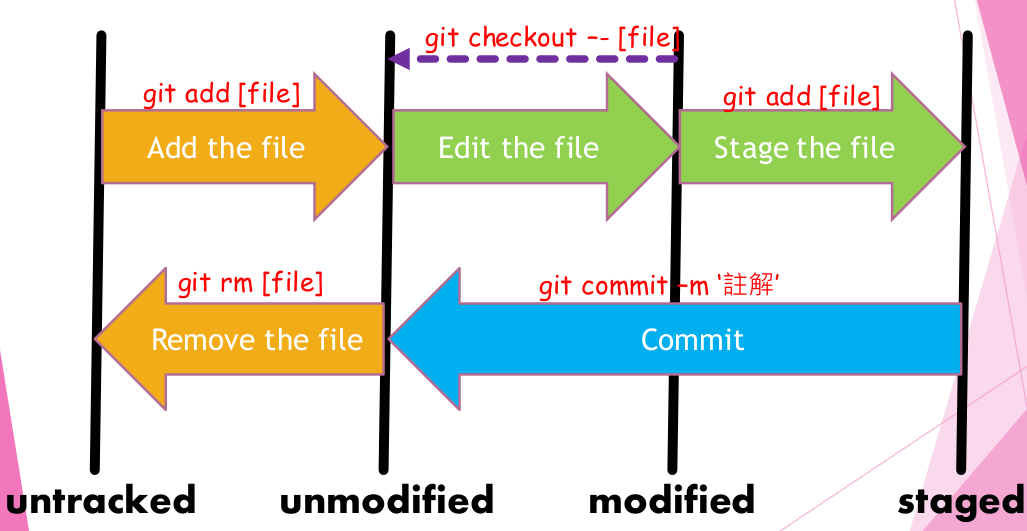
- **untracked**:檔案一開始都在這個狀態。
- **unmodified**:經由指令將``untracked``的檔案加入追蹤,或是,``staged``狀態的檔案經由commit,會到這個狀態。另外在這狀態的檔案可以藉由指令來取消追蹤。
- **modified**:檔案只要有改變就會到這個狀態,無論是在``unmodified``或是``staged``狀態。藉由指令可以放棄這些變更,回到之前的狀態。
- **staged**:在這個狀態的檔案,通常就是要準備要提交到新的版本中了。在此狀態的檔案一經過更改就會回到``modified``狀態。
------------------------------------------------------
安裝
====
在 Ubuntu/Debian 上,``sudo apt-get install git-core``
------------------------------------------------------
簡單操作
=======
初始化
-----
使用 ``git init`` 可在目前的目錄下初始化一個 git repository。
若需要建立一個沒有工作目錄 (working directory) 的 repository,可以使用 ``git init --bare`` 來初始化,所建立的 repository 僅有 git 容器內容,通常用於 repository server。
將檔案加入追蹤
------------
在工作目錄 (working directory) 下,git 不會自動追蹤新建立的檔案,必須透過 ``git add`` 指令先將檔案納入容器索引 (index) 才能 commit 進版本庫中。
在一個新的版本庫中新增一個檔案,並使用 ``git status`` 查看版本庫狀態。Git 會提示發現新的檔案,但是不會自動列入追蹤。
.. code-block:: prettyprint
```
$ echo "Hellow World" > new.txt
$ git status
# On branch master
#
# Initial commit
#
# Untracked files:
# (use "git add <file>..." to include in what will be committed)
#
# new.txt
nothing added to commit but untracked files present (use "git add" to track)
---------------------------
```
使用 ``git add`` 將檔案列入追蹤後,git 會顯示檔案預計在下一次提交時送出。
.. code-block:: prettyprint
```
$ git status
# On branch master
#
# Initial commit
#
# Changes to be committed:
# (use "git rm --cached <file>..." to unstage)
#
# new file: new.txt
#
--------------------------
```
``git add`` 指令後方除了檔名之外,也可以使用目錄名稱或是萬用字元當作輸入:
- ``git add .``:將目前所在目錄下的所有檔案 (包含子目錄) 加入追蹤。
- ``git add *.c``:將所有以「.c」結尾的檔案 (不包含子目錄) 加入追蹤。
- ``git add -p``:將目前所在目錄下的所有檔案的更改之處逐一顯示出來,並讓使用者確認是否要加入追蹤。
commit
------
**commit的觀念**:在完成一個功能或是修改一個功能後就commit,並且這次commit的程式碼是要能夠正常運行的。
如果一次commit多個功能,對於版本追蹤會有不好的影響,使用者會無法明確的知道是從哪一部份開始出錯。
輸入``git commit``之後
會有一個編輯介面供使用者輸入commit message
或直接輸入 ``git commit -m 'New function or something modified'``
要注意的是使用**單引號**包住commit message而非雙引號
將檔案取消追蹤
------------
在程式碼的編輯或編譯過程中,會出現一些不需要追蹤的檔案,例如:執行檔(\*.exe)、object file(\*.o)、vi的暫存檔(\*.swp)、gedit的暫存檔(\*.\*~)等。
git提供一個檔案幫助管理哪些檔案不需被追蹤,為``.gitignore``。在git中通常不會有``.gitignore``,必須由使用者新增並編輯。
只要在``.gitignore``中條列不想追蹤的檔案,並將``.gitignore``commit上去即可。若想要在``.gitignore``中輸入單行解,以``#``開頭。
:first commit: 如果已經確定該repo實作的內容,可以先針對repo建立``.gitignore``檔,對於管理上比較方便。
刪除檔案並取消追蹤
----------------
``git rm <filename>``直接取消追縱後,可以看到檔案已經被刪除了。
```
$ cat first.dat
first caca
$ git rm first.dat
rm 'first.dat'
$ git st
# On branch master
# Changes to be committed:
# (use "git reset HEAD <file>..." to unstage)
#
# deleted: first.dat
#
$ ls
$
```
如果刪錯要救援也沒有問題!!!
- ``git reset HEAD <filename>``:回復到unstaged(modified或unmodified)狀態。
- ``git checkout -- <filename>``:回復到unmodified狀態。就可以看到檔案已經回來了。此外,這個指令還可以放棄**前次commit之後所有的變更**,如果功能被寫爛了,想要重寫的話,這個指令很受用。
git厲害的地方,漸漸有感覺了吧!!
查看目前狀態
----------
``git status``
會列出目前尚未追蹤、有改變、移除或更名等檔案的狀態,同時會有提示告訴你,
該下什麼指令來作到什麼事。
像是status這類常用的指令,可以善用熱建設定。``git config --global alias.st status``,這個熱建設定指令,
往後藉由輸入``git st``來達到與``git status``相同的效果。
查看 log
--------
``git log`` 可以加上參數增加其他資訊
如
``git log --graph`` 為 branch 畫圖
``git log --all`` 列出所有 branch 等
log 中通常會包含 commit 編號、作者、日期和 log 內容等紀錄。
若暫不需詳細資訊,可以使用 ``--oneline`` 將每個 commit log 縮短至一行。
------------------------------------------------------
參考資料
=======
http://git-scm.com/doc
http://blog.longwin.com.tw/2009/05/git-learn-initial-command-2009/
