定義
=============
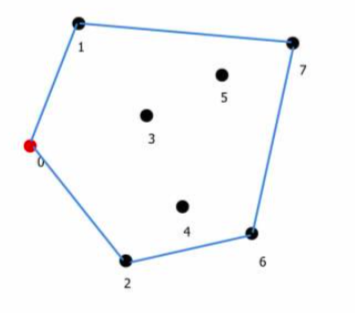
在散所有散佈點中,找出一個凸多邊形可以剛好包含所有的點
像下圖所示
演算法介紹
=============
有三種方法來找出凸多邊形
Brute Force
-------------
說明:
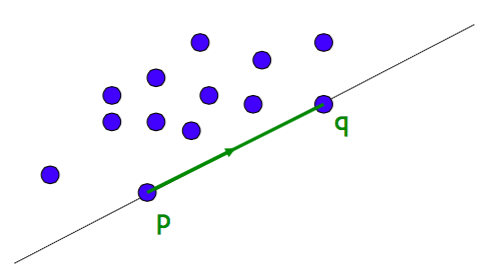
此方法為暴力解,先選擇任意兩個點構成線
假設其他的點都在那條線的左邊(or右邊, 固定一邊)
則此邊為我們要的邊
pseudo code:
```c++
Algorithm CH(P)
E←∅(* edge-list of CH(P) *)
for all ordered pairs (p,q) ∈ p×p, p≠q do
supporting ← true
for all points r ∈ P-{p,q} do
if r is on the right side of pq then supporting ← false
if supporting then add directed edge pq to E
From the (un-ordered) edge-list E, construct the list of vertices of CH(P) in CCW order in O(n) time. (How?)
end
```
複雜度:O(n³)
Graham-Scan
-------------
說明:
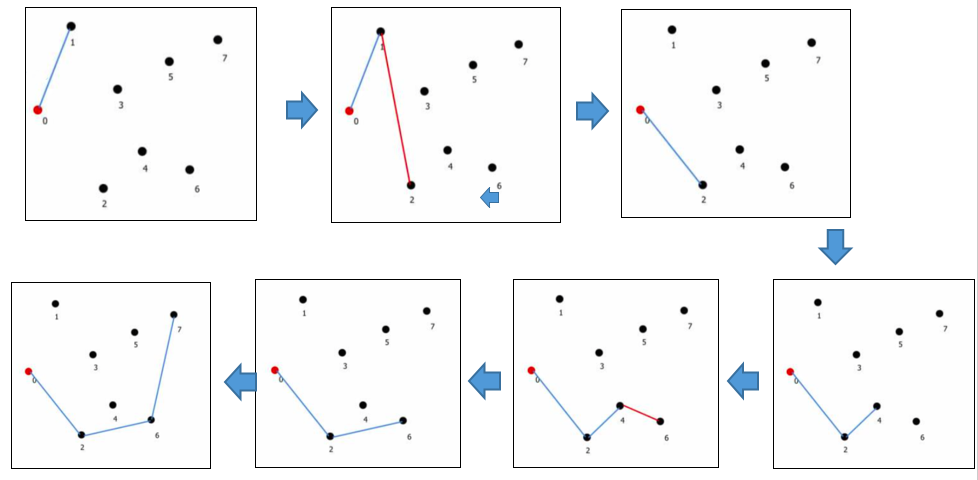
1.選定起始點,利用起始點跟其他點連線所構成的角度,去sort各個點
2.再開始一個一個點連線,假設
Andrew's Monotone Chain
----------------------------
>step1:將所有點按座標大小排序
>step2:將下半部圍起來
>step3:維持下半部不動,將上半部圍起來
>step4:刪去重複的起點
------------------------------
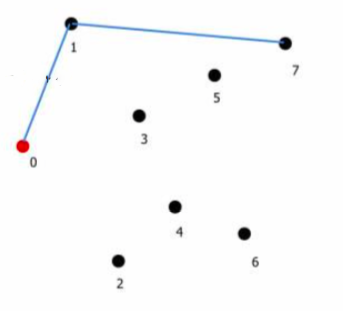
STEP1: 依照每個點的x座標進行排序
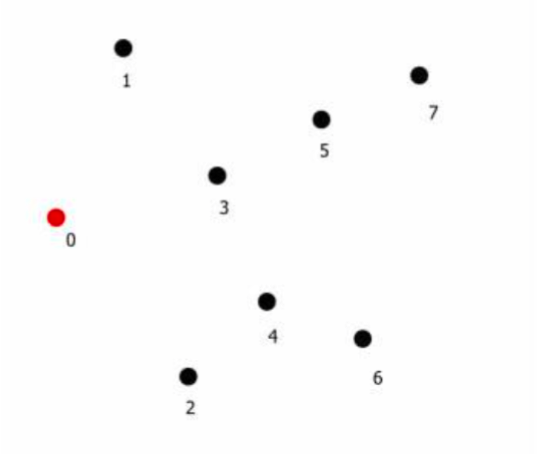
STEP2:
```c++
int m=0;
for(int i=0; i=2 &&
cross(CH[m-2], CH[m-1], P[i] <= 0) m--;
CH[m++] = P[i];
}
```
STEP3:
```c++
for(int i=N-2, t=m+1; i>=0; --i)
{
while(m>=t &&
cross(CH[m-2], CH[m-1], P[i] <= 0) m--;
CH[m++] = P[i];
}
```
STEP4:刪除最後一個點