定義
-------------------------------
dynamic programming (also known as dynamic optimization) is a method for solving a complex problem by breaking it down into a collection of simpler subproblems, solving each of those subproblems just once, and storing their solutions - ideally, using a memory-based data structure
[Reference](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dynamic_programming)
> DP全名為 Dynamic Programming (動態規劃) ,將問題切分多個子問題,簡化問題的複雜度,最後將所以子問題合併得到解答。
特性
---------------------------------
If the problem also shares an [optimal substructure](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Optimal_substructure) property, [dynamic programming](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dynamic_programming) is a good way to work it out.
[Reference](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Overlapping_subproblems)
> DP的題目有兩個重要的特性
> 1. Optimal Substructure (最佳子問題)
> 2. Overlapping Subproblem(子問題重疊)
> Q. Why memorization is ineffective in speed up a good divide-and-conquer algorithm such as MERGE_SORT ?
>
> sol)
> without overlapping. 如果沒有重疊的子問題,我們會發現時間複雜度並不會因為使用DP而降低,這是因為每次的子問題並沒有重複得部份!
Coin Change (錢幣交換)
-----------
**想法**
> dp[i]:i 價位是否可以湊的 (false/true)
> v[k]:第k種硬幣
>
> 如果i-v[k]價位可以湊得,那麼i必定也可以湊得
> If (dp[ i – v[k] ] == true) dp[ i ] = true;
**每種硬幣數量的差異**
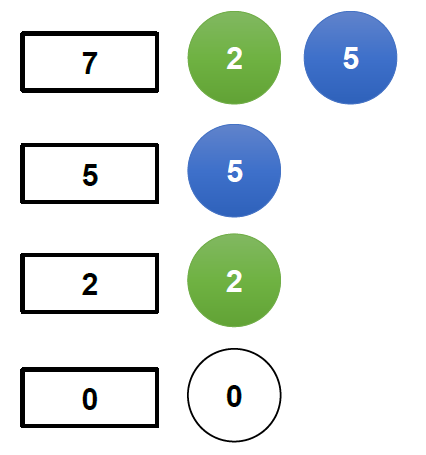
- 1 個硬幣
+ dp 的 index 由大到小掃過進行更新。
+ 圖示:N = 1,意即每個硬幣有 1 個。

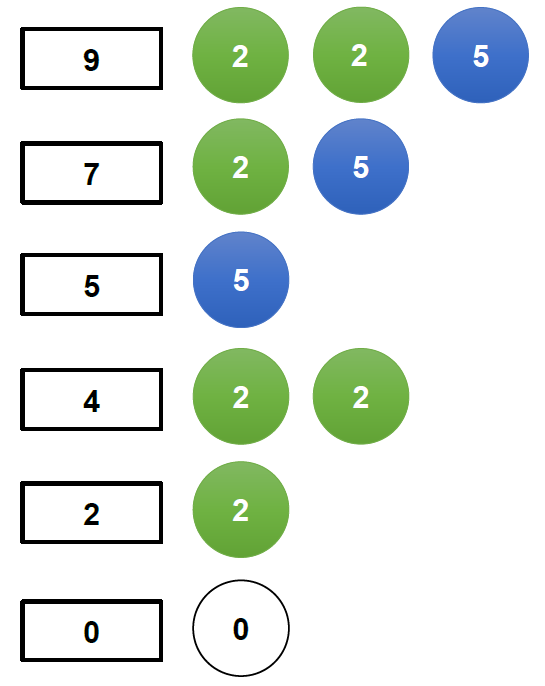
- N 個硬幣
+ dp 的 index 由大到小 N 次
+ 圖示:假設 N = 2,意即每個硬幣有 2 個。

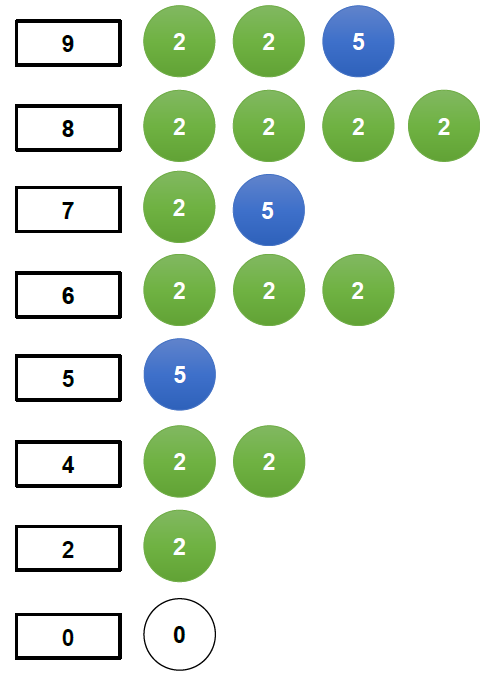
- 無限硬幣
+ dp 的 index 由小到大掃過進行更新。
+ 圖示:硬幣有無限多個。

**如果題目為湊得該價位有幾種方法,dp所紀錄的是方法數,dp[0]為1,不斷累加方法數到i==該價位**
> If (dp[ i - v[k] ] == true) dp[ i ] += dp[ i - v[k] ];
0/1 Knapsack Problem (0-1背包問題)
-------------
> Knapsack Problem:背包問題
> 將一堆物品塞進背包,要使背包裡的物品總價值最高,但背包有耐重限制,所以塞的太重的話,背包就會撐破。
>
> 0/1:
> 物品只會放進背包0個或1個,物品不可切割,所以只有不放或者全放兩種可能。
**想法**
> dp[m]:在m重量下目前的最佳價值
> v[i]:物品i的價值
> w[i]:物品i的重量
**類似硬幣交換的作法,不過dp[m]所紀錄的是目前使用i種物品在m重量可以得到的最佳價值,當發現某物品在相同重量下可以創造更佳的價值就進行更新**
> dp[m] = max( dp[m], dp[m - w[i]] + v[i] ); *
**圖示**
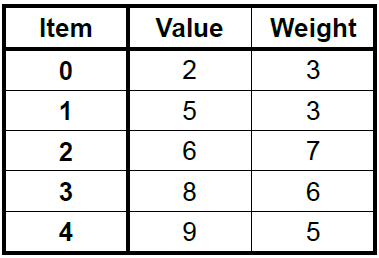
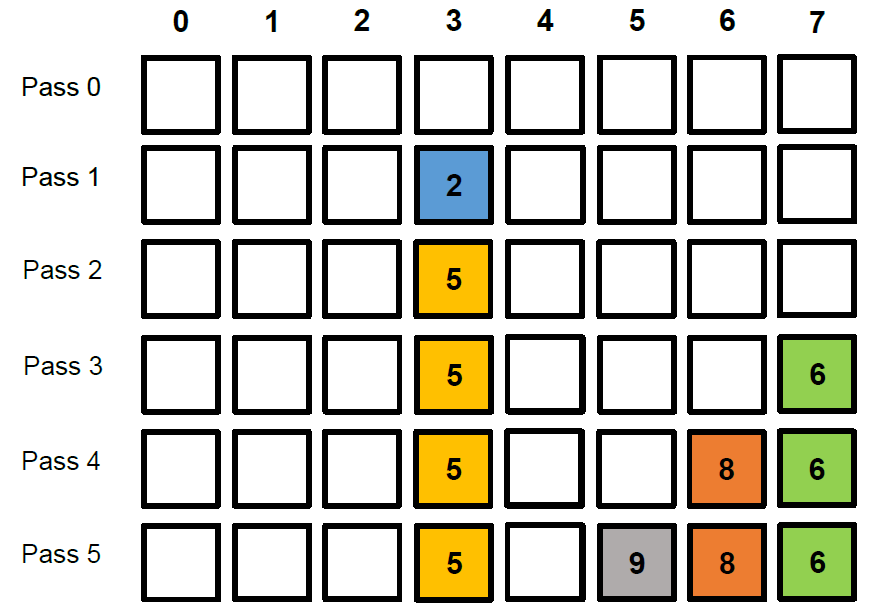
DP v.s Greedy Algorithm
============================
> Greedy 相較 DP 多出一個性質 - Greedy Choice,即每次只要挑選最佳的選擇,最後必定可以得到最佳解。
> 如果今天一件物品可以任意分割成數份,此問題變成為fractional背包問題,因為沒有最後一個物品塞不下的問題,每次只要挑選最高性價比(CP值)的物品,最終一定可以達到最高價值。
> 此問題與0/1背包問題差別就在於fractional背包問題有Greedy Choice特性,因此可以用速度更快的Greedy Algorithm來得到解。