acm/course/Map
Map
Introduce
欲使用map需先於程式開頭加上
Map通常用於將資料整合成一對一關係
其對關係為map<key, value>
其中一個value可以對應多個key
但是一個key只能對應一個value
當一個key尚未被指定值時 其對應value為0
例如常用的是用 int 將 string 做編號 :
map<int, string> m;
int n;
string s;
cin >> n >> s;
m[n] = s;
//Beware of the input order must suit the format of map而欲讀取資料的話需給予他iterator
注意:如果使用iterator時要符合格式.如果有格式不同的map則需另建一個新的iterator不可共用
map在資料存取中.key的為.first, value的為.second
例如要讀取所有的map的資料
.begin()是map第一筆資料的iterator
.end()是最後一筆資料的iterator的下一個位子
cout << "The datas stored in the map are: ";
for(it = m.begin(); it!= m.end(); it++)
{
cout << (*it).first << " " << (*it).second << endl;
}
//.begin() stands for the first data stored in the map或是如果只有要讀取”被你編號的某個” string
int search;
cout << "Input the number ID of the string you are looking for : ";
cin >> search;
cout << m[search] << endl;An fully executable program example :
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
map<int, string> m;
map<int, string>::iterator it;
int n;
string s;
int search;
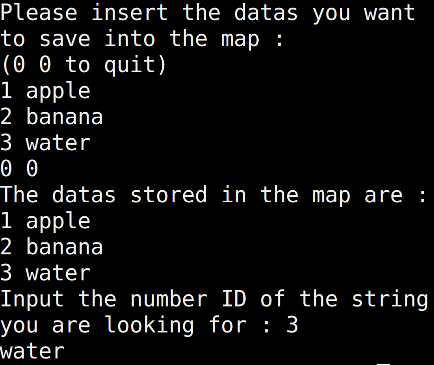
cout << "Please insert the datas you want to save into the map :" << endl;
cout << "(0 0 to quit)" << endl;
while(1)
{
cin >> n >> s;
if(n == 0 && s == "0")
break;
m[n] = s;
}
cout << "The datas stored in the map are : " << endl;
for(it = m.begin(); it!= m.end(); it++)
{
cout << (*it).first << " " << (*it).second << endl;
}
cout << "Input the number ID of the string you are looking for : ";
cin >> search;
cout << m[search] << endl;
}Output:
Member functions
.begin() / .end()
.begin()是map第一筆資料的iterator
.end()是最後一筆資料的iterator的下一個位子
.size()
可以用來檢測當前map裡有幾筆資料
例如
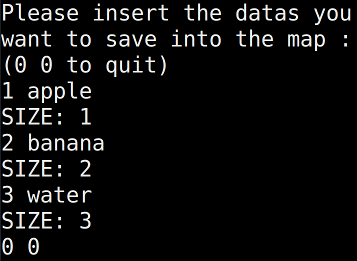
map<int, string> m;
int n;
string s;
while(1)
{
cin >> n >> s;
if(n == 0 && s == "0")
break;
m[n] = s;
cout << "SIZE: " << m.size() << endl;
}
.clear() / .empty()
.clear()是用來清空map裡所有資料的一個member function
.empty()是用來察看map裡的資料是否是空的的member function (returns boolean)
cout << "Is it empty ?" << endl;
if(m.empty())
cout << "Yes~" << endl;
else
cout << "No~~~~~" << endl;
cout << "Is it empty now?" << endl;
m.clear();
if(m.empty())
cout << "EMPTY!" << endl;
else
cout << "Nope" << endl;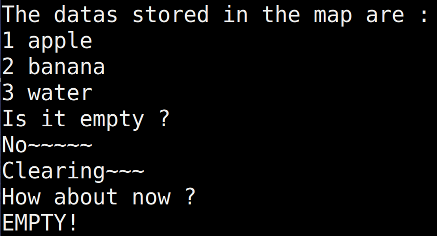
.find()
.find()是用來搜尋某筆map資料的iterator
在取得該筆map資料的iterator後可對其進行修改value
但是key因為是read-only所以無法對齊進行修改
格式: it = map.find(key);
Code example:
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
map<int, string> m;
map<int, string>::iterator it;
int n;
string s;
int search;
m[1] = "apple";
m[2] = "banana";
m[3] = "water";
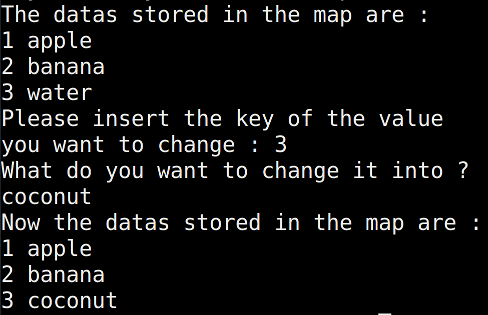
cout << "The datas stored in the map are : " << endl;
for(it = m.begin(); it!= m.end(); it++)
{
cout << (*it).first << " " << (*it).second << endl;
}
cout << "Please insert the key of the value you want to change : ";
cin >> search;
it = m.find(search);
cout << "What do you want to change it into ?" << endl;
cin >> (*it).second;
cout << "Now the datas stored in the map are : " << endl;
for(it = m.begin(); it!= m.end(); it++)
{
cout << (*it).first << " " << (*it).second << endl;
}
}Output:
.erase()
.erase()是用來清除特定iterator所存的map的資料
格式(有兩種):
Erase by iterator
配合上述的.find()使用
it = map.find(key);
map.erase(it);
Erase by key
map.erase(key);
Code example:
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
map<int, string> m;
map<int, string>::iterator it;
int n;
string s;
int search;
m[1] = "apple";
m[2] = "banana";
m[3] = "water";
cout << "The datas stored in the map are : " << endl;
for(it = m.begin(); it!= m.end(); it++)
{
cout << (*it).first << " " << (*it).second << endl;
}
cout << "Please insert the key of the value "<< endl;
cout << "you want to erase : ";
cin >> search;
m.erase(search);
cout << "Now the datas stored in the map are : " << endl;
for(it = m.begin(); it!= m.end(); it++)
{
cout << (*it).first << " " << (*it).second << endl;
}
}
A long code for you to look and execute for review(?)
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
map<int, string> m;
map<int, string>::iterator it;
void action_list()
{
cout << "Action List : (Input the number ID for the action)" << endl;
cout << "1. insert" << endl;
cout << "2. find" << endl;
cout << "3. size?" << endl;
cout << "4. erase" << endl;
cout << "5. clear" << endl;
cout << "6. emptied?" << endl;
cout << "7. print_map" << endl;
}
int main()
{
int n;
string s;
int action;
int search;
cout << "\033c";
cout << "Hi, this is a new map, you can now do several things to it" <<endl;
cout << "What do you want to do? " << endl;
action_list();
while(1)
{
cout << "Input action ID : ";
cin >> action;
if(action == 100)
{
cout << endl;
cout << "Program stopped" << endl;
break;
}
switch(action)
{
case 0:
cout << "\033c";
action_list();
break;
case 1:
cout << "\033c";
cout << "Please insert the datas you want to save into the map : (0 0 to quit)" << endl;
while(1)
{
cin >> n >> s;
if(n == 0 && s == "0")
break;
m[n] = s;
}
break;
case 2:
cout << "\033c";
cout << "Input the number ID of the string you are looking for : ";
cin >> search;
cout << m[search] << endl;
break;
case 3:
cout << "\033c";
cout << "There are " << m.size() << " datas now stored in the map" << endl;
break;
case 4:
cout << "\033c";
cout << "Please insert the key of the value you want to erase : ";
cin >> search;
m.erase(search);
break;
case 5:
cout << "\033c";
cout << "Map cleared to empty" << endl;
m.clear();
break;
case 6:
cout << "\033c";
if(m.empty())
cout << "Yeah ~ it's empty now..." << endl;
else
cout << "No ~ not empty yet ~" << endl;
break;
case 7:
cout << "\033c";
cout << "The datas now stored in the map are : " << endl;
for(it = m.begin(); it!= m.end(); it++)
{
cout << (*it).first << " " << (*it).second << endl;
}
break;
default:
cout << "\033c";
cout << "Error action input, type 0 to look at the action list" << endl;
break;
}
cout << endl;
cout << "Anything you also want to do ?" << endl;
cout << "(To end the program, you can type 100 now)" << endl;
cout << "(To review the action list please type 0)" << endl;
}
}