版本 4dad95195cb9a9bc63e16f5114ff4df9c4fe84b4
acm/course/Review1
Review 1
I/O
標準的輸入輸出有下列幾種指令
輸入:
scanf, gets, getchar, cin……
輸出:
printf, puts, putchar, cout….
但在比賽時由於需考慮效能所以多使用 scanf, printf 取代cin , cout
(因為cin, cout會回去呼叫scanf, printf)
比賽時常見的題型:
1.給測資的數量
Ex:
A+B problem
int tc,a,b;
scanf("%d",&tc);
while(tc--) {
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
printf("%d\n",a+b);
}2.以特定值(通常為 0)為中止條件
Ex:
Hi, input #
/* Until zero */
int n;
while(scanf("%d",&n)==1 && n) {
printf("Hi, %d.\n",n);
}3.以EOF(End of file)為中止條件
Ex:
Hi, input #
/* Until EOF */
int n;
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF) {
printf("Hi, %d.\n",n);
}若題目為指定測資終止條件,則以EOF作為終止條件
Ex:
scanf
while(scanf()!=EOF)
{
...
}fgets
while(gets()!=0)
{
...
}cin
while(cin >> x)
{
...
}1.在每個輸出後面加一個空白行
Ex:
A+B Problem
/*\n\n */
int a,b,cs=1;
while(scanf("%d%d",&a,&b)!=EOF){
printf("Case %d: %d\n\n",cs++,a+b);
}2.每個輸出被空行隔開(最後一個輸出後面不會有空行)
Ex:
/* Separated */
...
int a,b,cs=1;
while(
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b)!=EOF){
if(cs>1)putchar("\n");
printf("Case%d: %d\n",cs++,a+b);
}
...string token:
/*
char strtok(char *str,const char *delimiters);
str: 欲切割字串
delimiters: 分隔字符字串
return value: 指向當前切割字串之指標,若切割完畢則回傳NULL
*/
#include<cstring>
...
char str="Welcome to NCKU CSIE. 1*2(3456)78\9";
for( char *token = strtok( str," \"().*");token!=NULL;token=strtok(NULL," \"().")){
puts( token );
}| Output | ||
|---|---|---|
| Welcome | to | NCKU |
| CSIE | 1 | 2 |
| 3456 | 78 | 9 |
freopen:
/*freopen*/
...
freopen("f1.in","r",stdin);
freopen("f1.out", "w",stdout);
while(scanf(...)!=EOF){
printf(...);
}
...Time complexity and Sorting
###Time complexity
由於競賽題目多有時間限制,我們必須分析程式碼的時間複雜度,根據測資的數量判斷程式大概的執行時間,以避免超過題目的時間限制
𝑶(𝒏):
for(i=0; i<n; i++){
...
}𝑶(𝒏^2):
for(i=0; i<n ;i++)
for(j=0; j<n; j++){
...
}𝑶(𝟐^M):
int two(int n){
if(n < 2) return 1 << n;
return two(n - 1)+ two(n - 1);
}
/* maximum n=M */𝑂(1,000,000) 近似於 1 sec
###Sorting
「排序演算法」
顧名思義就是將一串資料,依照特定的規則排序的演算法。
####Selection sort(選擇排序法)
為日常生活中常用到的方法,不斷地找到最小值,再做移動,非常直觀。
時間複雜度為 𝑂(𝑛^2),且為不穩定排序。
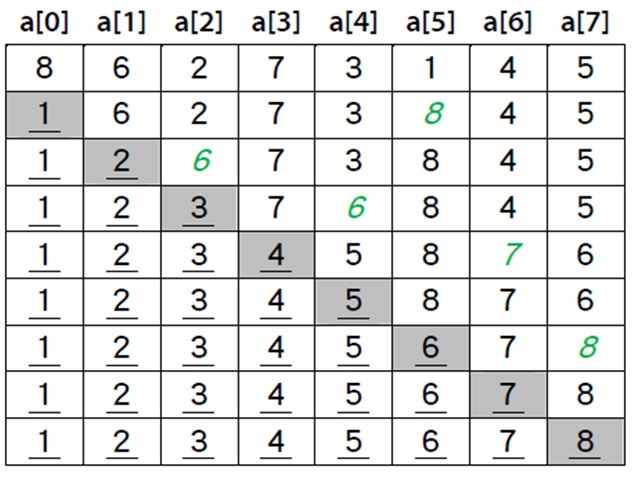
####Bubble Sort
「氣泡排序法」( or 泡沫排序法, 冒泡排序法…) 重複地走訪過要排序的數列,一次比較相鄰兩個元素,如果他們的順序錯誤就把他們交換過來。 時間複雜度 O(n^2),氣泡排序法為穩定排序。
