版本 f2b9ad26272bd58a9b9ff5c04157848760ca4350
Changes from f2b9ad26272bd58a9b9ff5c04157848760ca4350 to current
---
title: ARMv8
categories: arm, armv8, arm64, embedded
categories: arm, armv8, arm64, embedded, cortex-a35, cortex-a53, cortex-a57, cortex-a72
...
ARMv8架構介紹
=====================================
.. image:: http://www.arm.com/zh/images/roadmap/V5_to_V8_Architecture.jpg
.. image:: /embedded/evolution_arm_arch.png
# ARMv8架構介紹
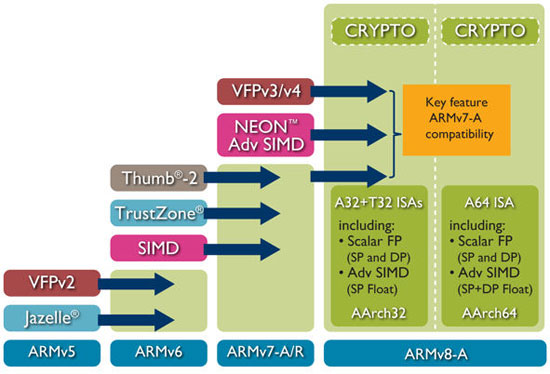
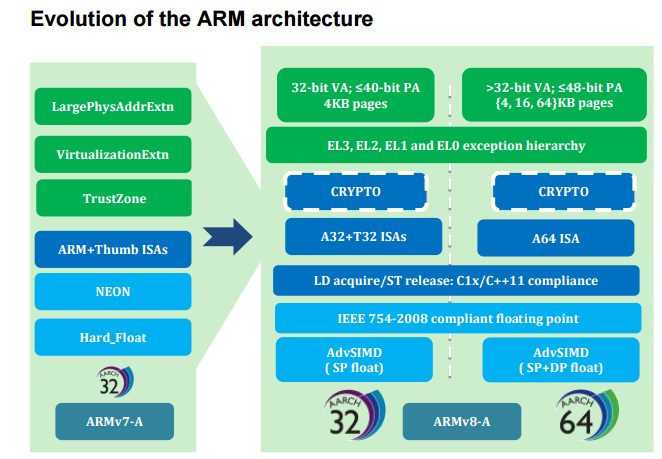
ARMv8架構有一個重要的特點是他與其之前的架構相容。
Execution state
----------------------------
- AArch64 - 64-bit Execution state.
- 提供 31組 64-bit 的通用暫存器
- 提供 64-bit Program Counter(PC), Stack-Poiner(SP)與Exception-Link-Register (ELR)
- 定義最多四種(EL0 - EL3)特權模式
- 支援 64-bit 虛擬地址
- 定義一組PSTATE來保存PE state
- AArch32 - 32-bit Execution state
## Execution state
* AArch64 : 64-bit Execution state
- 提供 31組 64-bit 的通用暫存器,其中 X31 當 Procedure Link Register 使用
- 提供 64-bit Program Counter(PC), Stack-Poiner (SP )與 Exception-Link-Register (ELR)
- 定義最多四種 (EL0 - EL3) 特權模式
- 支援 64-bit 虛擬地址
- 定義一組 PSTATE 來保存 PE state
- 沒有協處理器的觀念
- 提供 16組 32-bit 的通用暫存器
- 提供 1組 ELR,作為從Hyp-Mode的Exception返回之用
- 提供 A32(相容ARMv7 ARM)與 T32(相容ARMv7 Thumb)兩種指令集
- 使用32-bit 虛擬地址
- 使用單一的CPSR來保存PE state
* AArch32 : 32-bit Execution state
- 提供 16組 32-bit 的通用暫存器
- 提供 1組 ELR,作為從 Hyp-Mode 的 Exception 返回之用
- 提供 A32 (相容ARMv7 ARM) 與 T32 (相容 ARMv7 Thumb) 兩種指令集
- 使用 32-bit 虛擬地址
- 使用單一的 CPSR 來保存 PE state
- AArch32 只支援 CP10, CP11, CP14, and CP15
在A32與T32中做切換只要透過BX即可,但要在AArch32與AArch64間做切換只能透過Exception
在 A32 與 T32 中做切換只要透過BX即可,但要在 AArch32 與 AArch64 間做切換只能透過 Exception
.. image:: http://loda.hala01.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/12/image005.png

(圖片來自loda大大的blog)
AArch64 指令集 (instruction set) 介紹
=====================================
# AArch64 指令集 (instruction set) 介紹
ARMv8-A_Architecture_Reference_Manual P.111
系統層級架構 (System Level Architecture)
=====================================
# 系統層級架構 (System Level Architecture)
ARMv8-A_Architecture_Reference_Manual P.1405
例外層級 (Exception levels)
----------------------------
## 例外層級 (Exception levels)
ARMv8-A_Architecture_Reference_Manual P.1408
- ARMv8-A架構定義了四個例外層級,分別為EL0到EL3,其中數字越大代表特權(privilege)越大。
- EL0: 無特權模式(unprivileged)
- EL1: 作業系統核心模式(OS kernel mode)
- EL2: 虛擬機器監視器模式(Hypervisor mode)
- EL3: TrustZone® monitor mode
- 要提升到較高層級需要透過exceptions(如: 中斷、page faults等)。
- EL0 => EL1: SVC (system call)
- EL1 => EL2: HVC (hypervisor call)
- EL2 => EL3: SMC (secure monitor call)
- 在轉換時會將返回位址(return address)紀錄在例外連結暫存器ELR(Exception-Link-Register)。
- 每個EL會有個別的SP(stack pointer)
- 根據目前架構,由下層系統的Execution State決定上層系統所在模式
- 若下層系統為32bits則上層只能為32bits,反之若為64bits則上層可為32bits or 64bits
.. image:: /embedded/armv8 arch.png

安全性狀態 (Security state)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
## 安全性狀態 (Security state)
ARMv8-A架構提供兩種安全性狀態,他們有個別的實體記憶體定址空間(Secure physical address space)。
- 安全狀態(Secure state): PE可以存取安全及不安全的實體定址空間
- 安全狀態(Secure state): PE可以存取安全及不安全的實體定址空間,有EL0.EL1.EL3
- 不安全狀態(Non-Secure state): 只能存取不安全的實體定址空間
- 不安全狀態(Non-Secure state): 只能存取不安全的實體定址空間,有EL0.EL1.EL2
Extension.png
(from: Hardware Support Virtualization (國立清華大學))
虛擬化 (Virtualization)
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
## 虛擬化 (Virtualization)
這邊的虛擬化只有支援有實現EL2的架構。以下為其基礎模型:
這邊提到的虛擬化為**有實現EL2架構**的系統。以下為其基礎模型: (manual D1.5 Virtualization)
- 一個跑在EL2的Hypervisor負責切換跑在EL1、EL0的virtual machines
- 一些跑在virtual machines上(在EL1中)的Guest OS
- 每個Guest OS上跑在EL0的應用程式
每個VM會被Hypervisor指定一個VMID。
EL2只會實現在 Non-secure state,並負責:
- 提供虛擬值給少數特定的暫存器(1)。Guset OS 或其上的應用程式讀取這些暫存器時會得到虛擬的值。
- Trapping: 當在做記憶體管理及存取其他大多數的暫存器((1)之外的)時會產生exception並由EL2處理。
- Routing interrupt: 將中斷分配給
- 現在的Guest OS
- 現在沒在執行的Guest OS
- hypervisor
(以上會在個別的章節特別探討)
實現EL2包含以下實作:
- Hypervisor Call (HVC) exception
- Traps to EL2
- 虛擬中斷:
- 包括:
- Virtual SError
- Virtual IRQ
- Virtual FIQ
- 所有虛擬中斷會由EL1處理
- 每個虛擬中斷可由EL2個別啟用
- 每個虛擬中斷都會有其對應的實體中斷
- 當一個虛擬中斷被啟用時,其對應的實體中斷會由EL2處理(除非EL3指定他要處理)
指令與例外處理暫存器 (Registers for instruction processing and exception handling)
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
## 指令與例外處理暫存器 (Registers for instruction processing and exception handling)
### 通用暫存器
31 個通用暫存器R0-R30。可以作為64-bit暫存器X0-X30或是 31個 32-bit暫存器W0-W30來被存取。
SP暫存器 (stack pointer registers)
......................................
### CPSR

- 與 armv7 的比較 (可參考 [loda armv8-與-linux的新手筆記](http://loda.hala01.com/2014/12/armv8-%E8%88%87-linux%E7%9A%84%E6%96%B0%E6%89%8B%E7%AD%86%E8%A8%98/) ,以下圖片有些來自此網站)

- aarch32 多了Bit 20:IL (Illegal Execution State bit)
- aarch64 多了Bit 9:E 被 D取代,並少了 IT,GE
- M(mode): 現在處理器運行的模式
- M[4]: 0表示現在是AArch64,1則表示現在是在AArch32
- M[3:0]: Current processor mode
- 再AArch32下mode與Armv7下的表示相同,在AArch64下則如下圖所示:

- IT[7:2], bits [15:10] 與 IT[1:0] (AArch32), bits [26:25]: T32 IT (If-Then) instruction
### Process state PSTATE

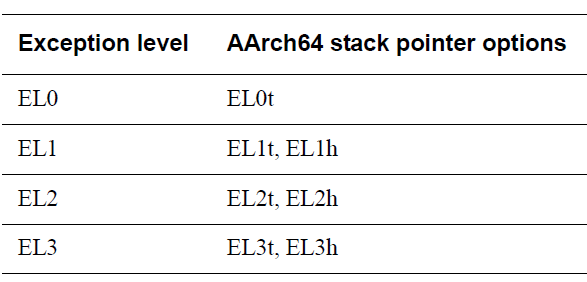
### SP暫存器 (stack pointer registers)
- 每個例外層級都有專用的SP: SP_EL0 ~ SP_EL3 (SP_EL2、SP_EL3只有在有實現該層的架構時才會存在)
- 例外(exception)發生時,預設會使用例外目標層級的SP_ELx (例如例外目標為EL1就會選用SP_EL1)
- 也可透過更新PSTATE.SP.選用SP_EL0
- SPSel, Stack Pointer Select SP, bit [0]
- 0 Use SP_EL0 at all exception levels.
- 1 Use SP_ELx for exception level ELx.
- 用msr、mrs來存取
- 可以透過t(SP_EL0)、h(SP_ELx)的後綴表明SP的例外層級
.. image:: /embedded/sp_th.png
SIMD 與浮點暫存器
......................................
- SPSel, Stack Pointer Select: 可以透過MSR, MRS存取來設定要用哪個SP
- SP, bit [0]:Stack pointer to use.
- 0 Use SP_EL0 at all exception levels.
- 1 Use SP_ELx for exception level ELx.
### SIMD 與浮點暫存器
- 共用32個128位暫存器V0-V31
- 可作為以下來存取
- 32 doubleword (64-bit) registers, D0-D31.
- 32 word (32-bit) registers, S0-S31.
- 32 halfword (16-bit) registers, H0-H31.
- 32 byte (8-bit) registers, B0-B31.
程式狀態儲存暫存器SPSRs (Saved Program Status Registers)
............................................................................
### 程式狀態儲存暫存器SPSRs (Saved Program Status Registers)
- 在例外發生時用來儲存PE的狀態
- 在AArch64中,每個例外層級都有一個SPSR: SPSR_EL1 ~ SPSR_EL3
- 在例外發生時,會把PE的狀態存在目標層級的SPSR中
- 當從例外返回時,PE的狀態會從SPSR中載入
.. image:: /embedded/SPSR.png
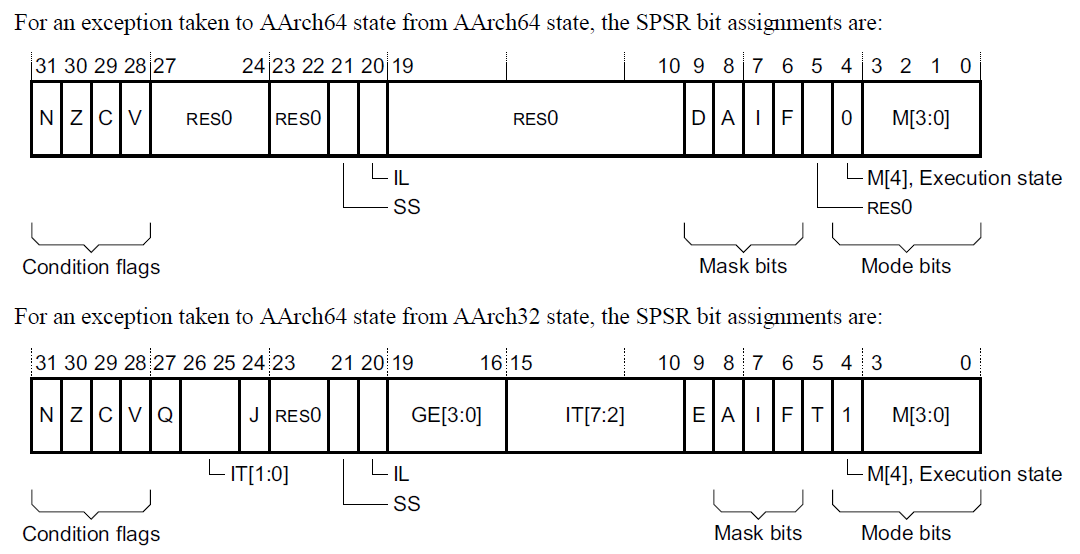
(請對照 P.1418)
例外連結暫存器ELRs (Exception Link Registers)
.............................................
### 例外連結暫存器ELRs (Exception Link Registers)
- 保存例外返回的位置
- 例如: 當例外目標為EL1時,返回的位置會存在ELR_EL1中
- 從例外返回時,會載入ELR的位只到PC中
- 當例外是從 AArch32 到AArch64 時 ELR bits[63:32]被設為0。
### Syndrome Register
- 保存觸發exection的原因(可用來作instruction emulation,請對照 [xvisor-instruction-emulate](http://wiki.csie.ncku.edu.tw/embedded/xvisor#xvisor-instruction-emulate)服用)
虛擬記憶體系統架構 (Virtual Memory System Architecture)
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- e.g.
- esr_el2
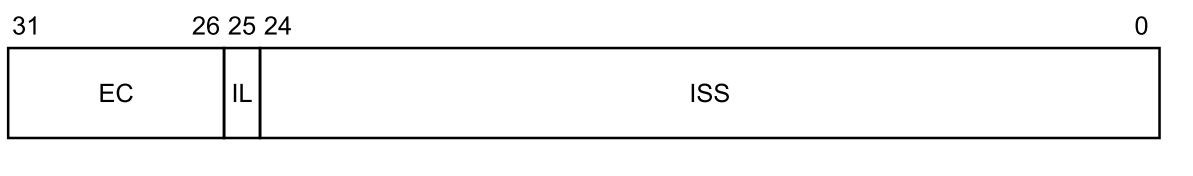
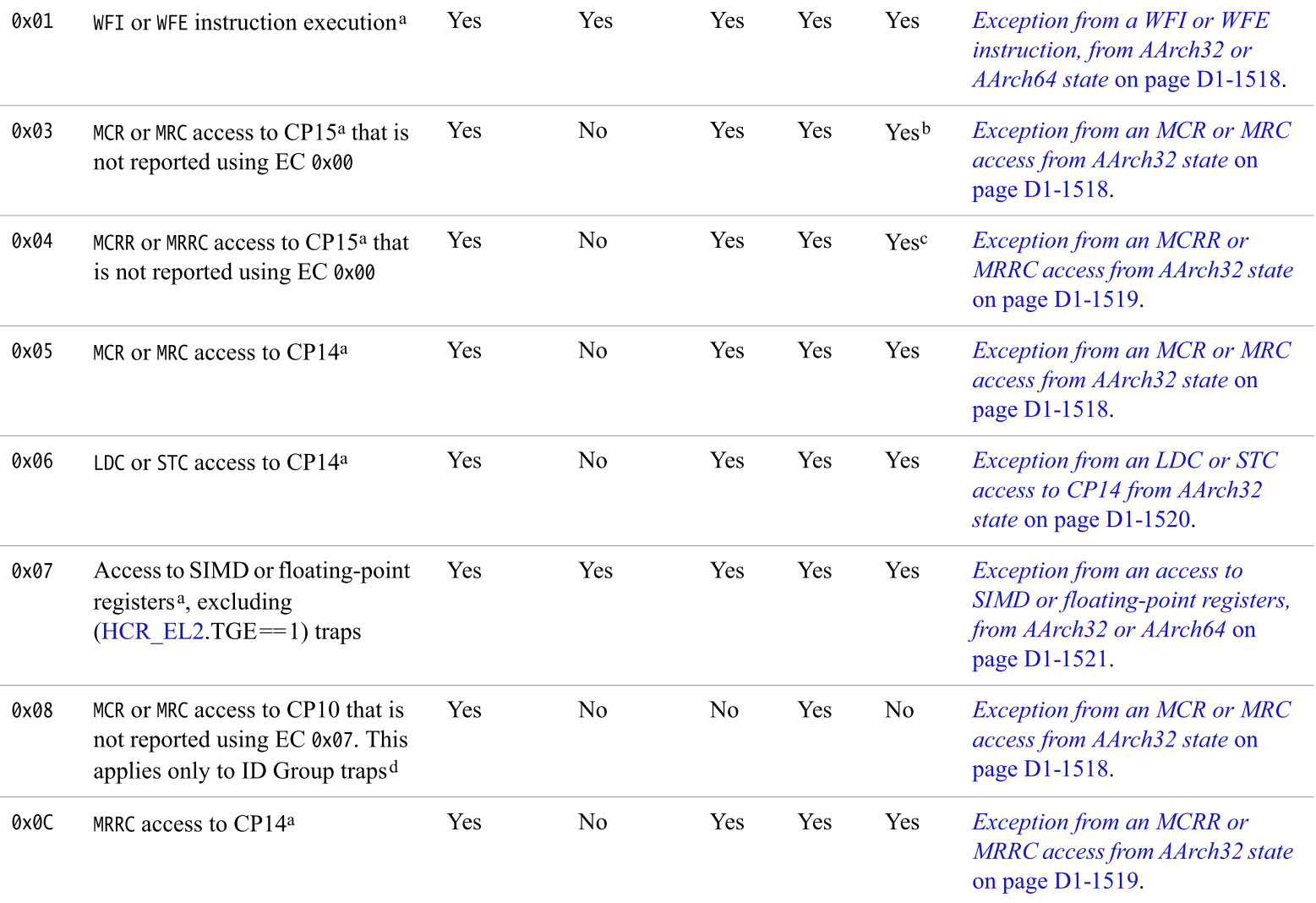
- ec 編碼(節錄,請對照manual D8.2.25 ESR_EL2, Exception Syndrome Register (EL2) 章節):
# 虛擬記憶體系統架構 (Virtual Memory System Architecture)
ARMv8-A_Architecture_Reference_Manual P.1707
概述
......................................
## 概述
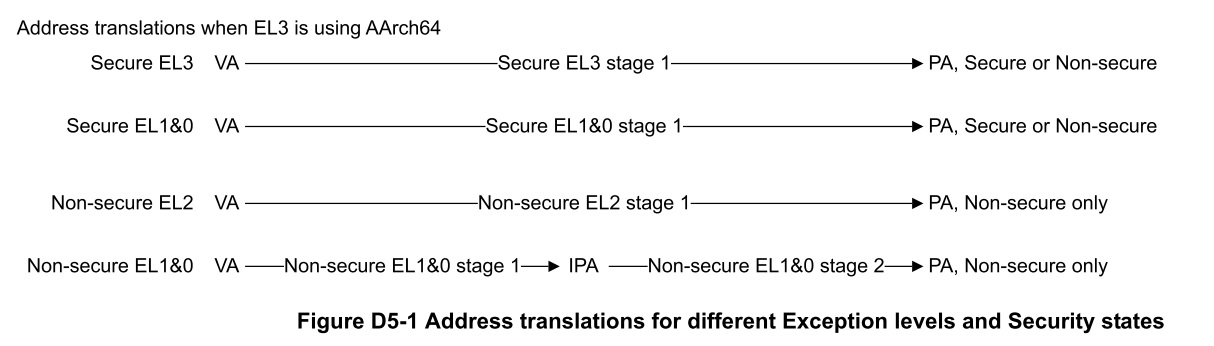
Virtual Memory System Architecture簡稱VMSA。 VMSA有記憶體管理單元(MMU)來負責控制地址轉換(address translation)。
地址轉換在不同例外層級與安全狀態之間是獨立的。
.. image:: /embedded/mm.jpg
- 虛擬地址Virtual Address (VA)
- instruction 使用的地址(PC, LR, ELR, SP 保存的地址)
- 最大為48 bits
- EL1&0 的VA範圍分為兩個子範圍。 0x0000_0000_0000_0000 ~ 0x0000_FFFF_FFFF_FFFF 及 0xFFFF_0000_0000_0000 ~ 0xFFFF_FFFF_FFFF_FFFF。
- 中間實體地址Intermediate Physical Address (IPA)
- 當提供二階地址轉換時,作為第一階的輸出,第二階的輸入。
- 當只提供一階地址轉換時,IPA即為PA
- 最大為48 bits
- 實體地址Physical Address (PA)
- 在實體記憶體MAP中的位址
- EL3 和 Secure EL1 例外層及提供獨立的Secure、Non-secure實體定址空間。
- Secure state存取VA可以被轉換成Secure或Non-secure的實體定址空間
- Non-secure state時虛擬地址只能對應到Non-secure state的實體定址空間
- 地址轉換:
- Translation table base register (TTBR) 指向translation table的起始位置。
- EL1&0 stage 1 translation 需要兩個translation table,一個是對低位址定址空間,一個是對高位址。
.. image:: /embedded/TTBR01.jpg
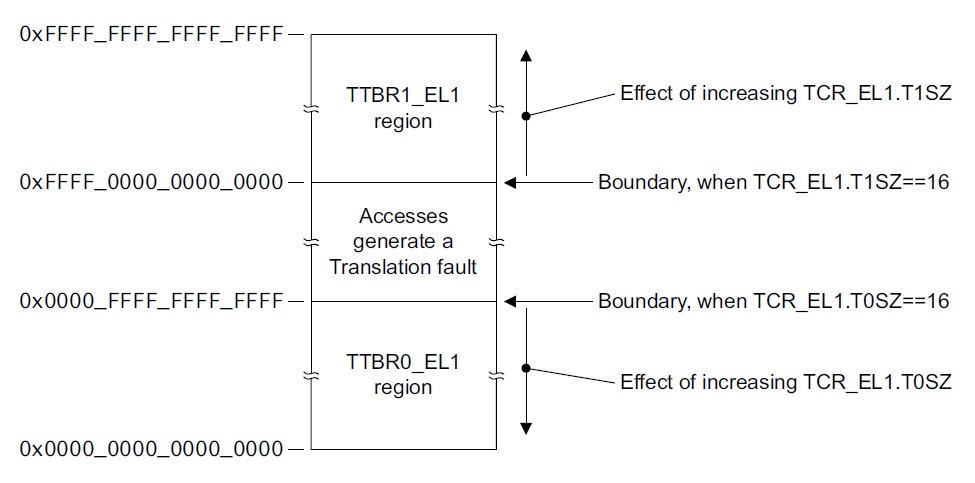
- [stackoverflow](http://stackoverflow.com/questions/14460752/linux-kernel-arm-translation-table-base-ttb0-and-ttb1)
- TLB 可以cache Translation table entries
地址轉換階級控制 (Controlling address translation stages)
............................................................................
## 地址轉換階級控制 (Controlling address translation stages)
- 不同的implementation,translation stages的實作也會不同
.. image:: /embedded/AArch64_translation_stages.jpg
- 對每個地址轉換階級:
- A system control register(CR) bit 啟用該層地址轉換
- A CR bit 決定轉換表查找的 endianness
- Translation Control Register (TCR)控制該層地址轉換
- 若該層VA支援分開的VA 範圍(EL0、EL1),則提供 Translation Table Base Register (TTBR)給每個子範圍。即:
- 一個TCR
- 一個TTBR給每個VA子範圍
- TTBR保存查找所需的base address
- MMU相應的系統控制暫存器
.. image:: /embedded/CR.jpg
- stage 2 translation 是ARM 對記憶體虛擬化的擴展。 虛擬化必須讓Guest OS不能存取hypervisor的記憶體空間。在沒有虛擬化擴展的情況下,是透過"shadow page tables"來完成這個要求。
- Shadow page tables: hypervisor 建立屬於自己的page table,當他發現有page fault時,會讀取OS所建立的page table及OS map的地址,再實際map到MMU使用的page table,因此只有hypervisor實際能把VA轉換成PA。缺點是複雜及耗能。
- With ARM Virtualization extensions: 將上面的動作交給硬體來做,hypervisor讓硬體認為guest OS產生的實體地址為虛擬地址,然後再以此地址(IPA)做第二階translation。
.. image:: http://www.futurechips.org/wp-content/uploads/2013/03/stage-1-translation-3.png

(圖片來自http://www.futurechips.org/understanding-chips/arm-virtualization-part-2-memory-interrupts.html)
記憶體轉換顆粒大小(Memory translation granule size) (暫譯)
............................................................................
## 記憶體轉換顆粒大小(Memory translation granule size) (暫譯)
- 定義了:
- 單一轉換表的最大大小
- page size
- VMSAv8-64支援4KB, 16KB, and 64KB的translation granule sizes
.. image:: /embedded/granule size.jpg
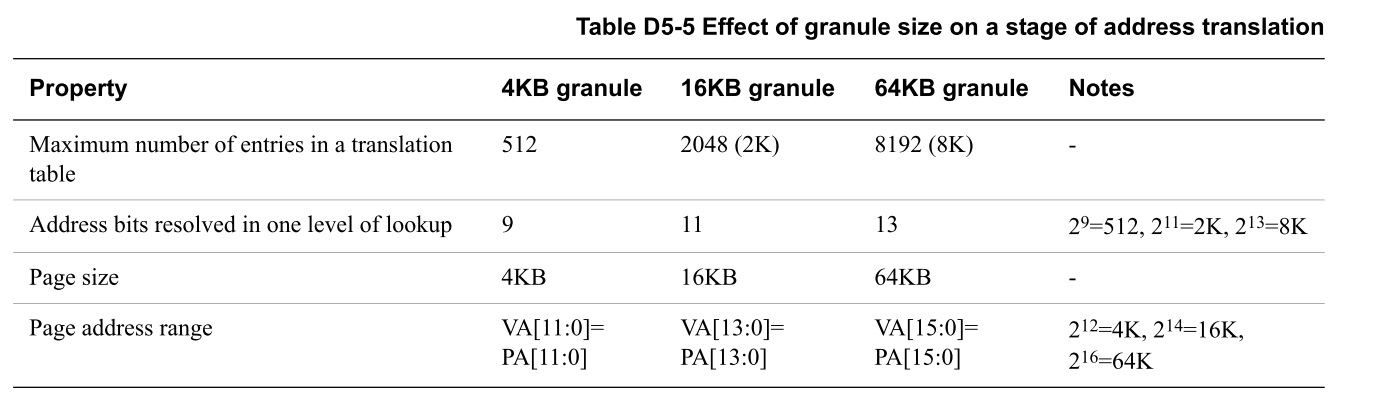
- granule size決定了page及一次查找可以轉換的bit數
.. image:: /embedded/4KB.jpg
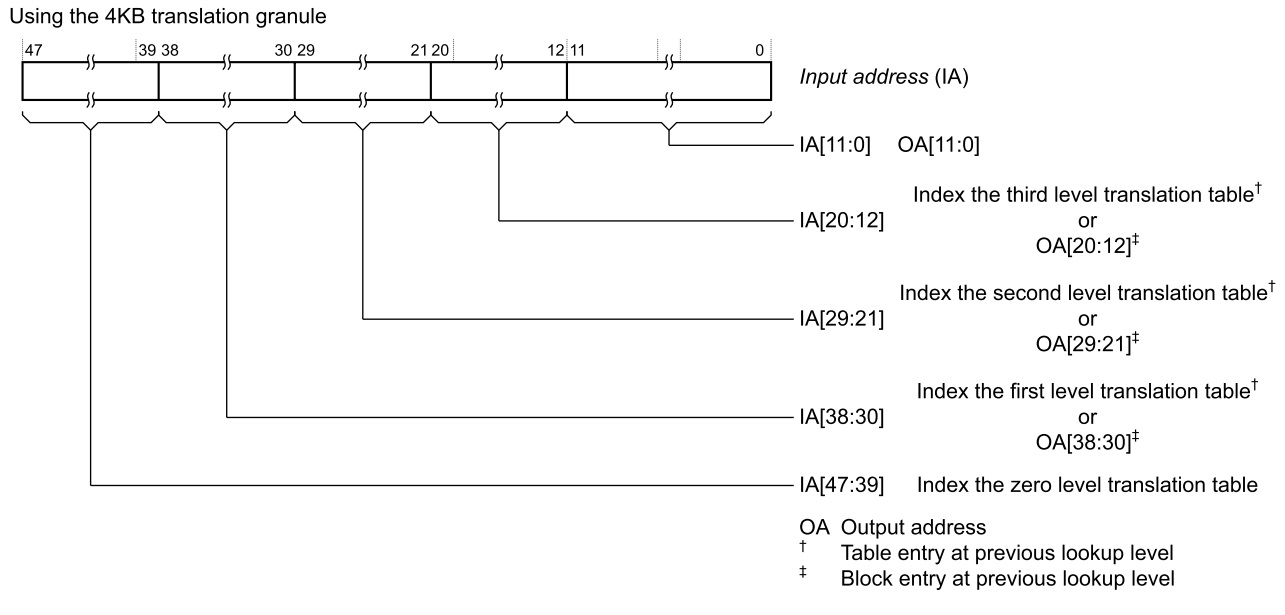
.. image:: /embedded/16KB.jpg
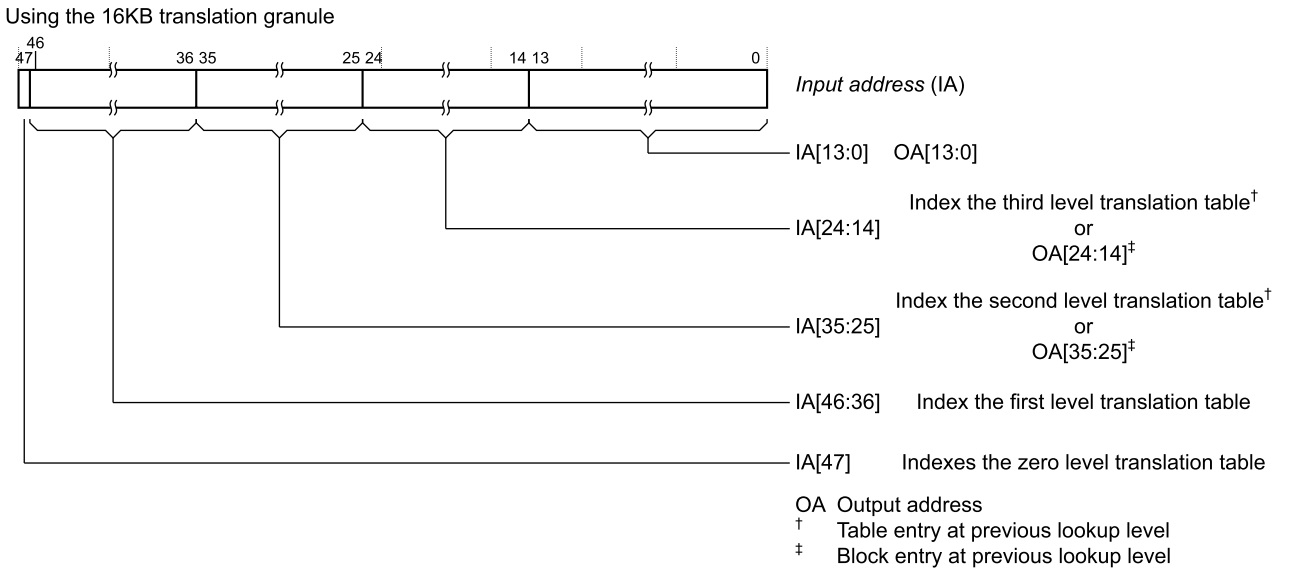
.. image:: /embedded/64KB.jpg
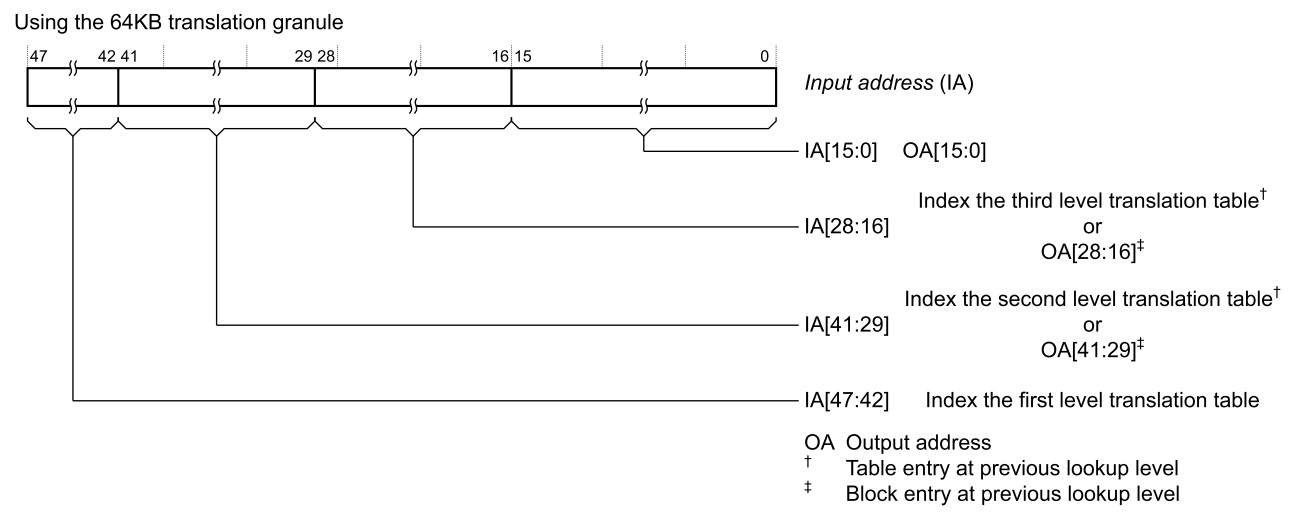
Translation table walks
.................................................................
## Translation table walks
- 從讀取轉換表開始,TTBR會保存該階級的base address
- 每次查找會返回一個descriptor標明以下其中一個情況:
- 該entry是walk的最後一個entry。此entry包含該次存取的OA、權限及屬性。
- 需要額外層級的查找。 此entry包含該層級查找的translation table base address。
- descriptor提供final translation的 hierarchical attributes
- invalid: Translation fault
.. image:: /embedded/stage of address translation.jpg
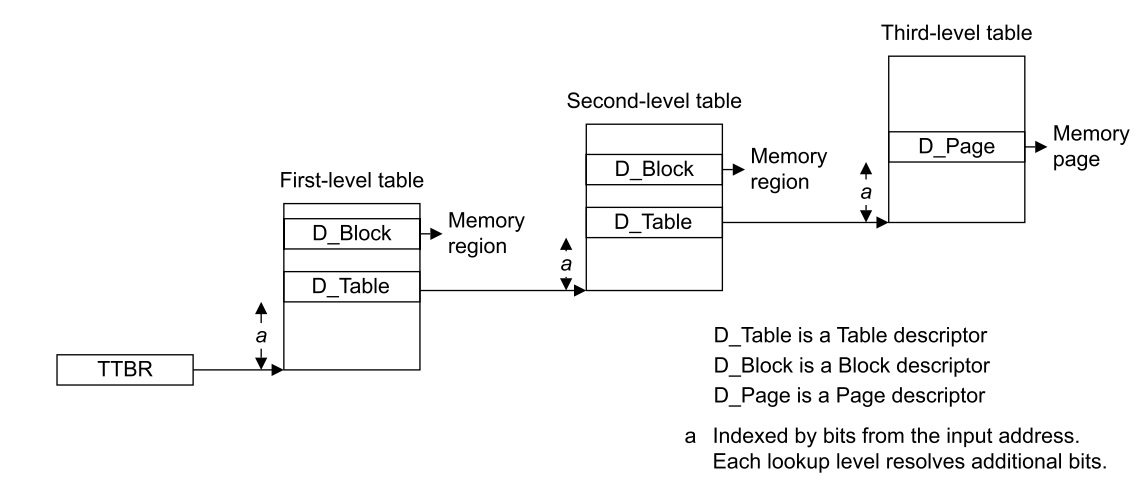
通用計時器 (The Generic Timer)
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
地址轉換流程:
- stage 1 translation table walk for a 48-bit input address 與 39-bit input address
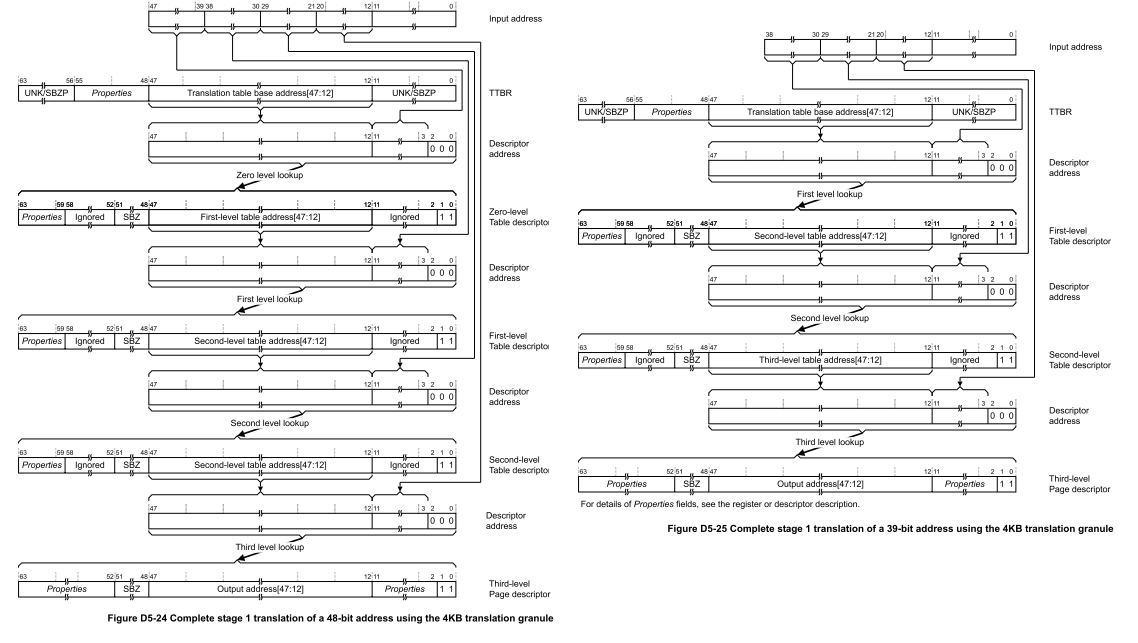
# 通用計時器 (The Generic Timer)
ARMv8-A_Architecture_Reference_Manual P.1855
reference
=====================================
* `ARMv8-A_Architecture_Reference_Manual_(Issue_A.a) (需登入)<http://infocenter.arm.com/help/index.jsp?topic=/com.arm.doc.ddi0487a.e/index.html>`_
* `loda armv8-與-linux的新手筆記<http://loda.hala01.com/2014/12/armv8-%E8%88%87-linux%E7%9A%84%E6%96%B0%E6%89%8B%E7%AD%86%E8%A8%98/>`_
* http://www.slideshare.net/badaindonesia/linux-on-arm-64bit-architecture?related=1
* `Principles of ARM® Memory Maps <http://infocenter.arm.com/help/topic/com.arm.doc.den0001c/DEN0001C_principles_of_arm_memory_maps.pdf>`_
* http://www.futurechips.org/understanding-chips/arm-virtualization-part-2-memory-interrupts.html
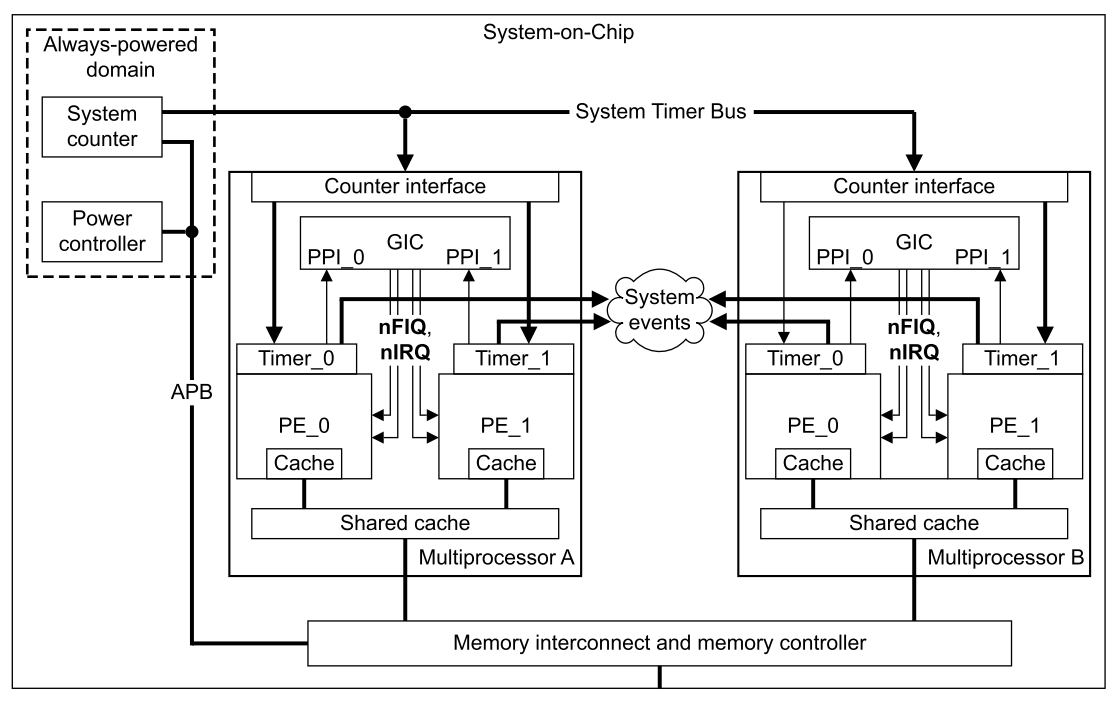
- 提供系統計數器來測量時間 (in real-time)
- 支援虛擬計數器來測量在特定虛擬機器上虛擬時間(virtual-time)
- Timer, 它可以用在週期時間之後觸發event
- 可用來當count-up或者 count-down timers
- 可在real-time或者virtual-time上做操作
## 系統計數器 (System counter)
- Width: 至少56-bits
- Frequency: 1-50MHz,支援多個可選擇的運作模式,如在低頻率下一次增加較多的數量,通常用來省電(power-saving)。
- Roll-over: 大於40年
- Accuracy: ARM沒有指定要求精度,但建議誤差不要超過10秒/24小時
- Start-up: 從0開始
- 它必須被實作在一個always-on power domain
- 初始化: 必須在系統booting時設定其頻率,可以寫入CNTFRQ 暫存器來做設定。
## 實體計數器 (physical counter)
PE有一個實體計數器包含系統計數器的count. (保存在CNTPCT暫存器中)
- CNTPCT:
- Secure EL1 modes及Non-secure Hyp mode隨時可以存取
- Non-secure EL1 mode CNTHCTL.EL1PCTEN 被設為1時才能存取,否則會被trap到Hyp
- 另外,當CNTKCTL.EL0PCTEN 被設為1時,在當下的安全性狀態的EL0、EL1就可以存取
- CNTKCTL 比 CNTHCTL有較高的優先權
## 虛擬計數器 (virtual counter)
- CNTVCT 暫存器保存現在的虛擬計數器count
- virtual counter = physical counter - 64-bit virtual offset.
- 當執行在Non-secure EL1 or EL0時, virtual offset值相對目前的virtual machine
# Reference
* [ARMv8-A_Architecture_Reference_Manual_(Issue_A.a) (需登入)](http://infocenter.arm.com/help/index.jsp?topic=/com.arm.doc.ddi0487a.e/index.html)
* [ARMv8 與 Linux 的新手筆記](http://loda.hala01.com/2014/12/armv8-%E8%88%87-linux%E7%9A%84%E6%96%B0%E6%89%8B%E7%AD%86%E8%A8%98/)
* [Linux on ARM 64-bit Architecture](http://www.slideshare.net/badaindonesia/linux-on-arm-64bit-architecture)
* [Principles of ARM® Memory Maps](http://infocenter.arm.com/help/topic/com.arm.doc.den0001c/DEN0001C_principles_of_arm_memory_maps.pdf)
* [ARM Virtualization Extensions – Memory and Interrupts](http://www.futurechips.org/understanding-chips/arm-virtualization-part-2-memory-interrupts.html)
* [Porting to 64-bit ARM](http://community.arm.com/servlet/JiveServlet/previewBody/8453-102-5-16300/Porting%20to%20ARM%2064-bit.pdf)
* [Hardware Support Virtualization (國立清華大學)](http://www.google.com.tw/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=6&ved=0CEcQFjAF&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.cs.nthu.edu.tw%2F~ychung%2Fslides%2FVirtualization%2FVM-Lecture-7-2-Hardware%2520support-ARM.pptx&ei=IV9EVb7BMcX6mQXtqIHoAw&usg=AFQjCNGHnO4BuuVHMSKBVCmZJTVJuzclEg&sig2=3_yUFkFNMRKwXlEGAY481Q)
