版本 f554b9b2082e206c32880d7354e17c6785c5d24f
acm/course/Map
Map
Introduce
欲使用map需先於程式開頭加上
Map通常用於將資料整合成一對一關係
其對關係為map<key, value>
其中一個value可以對應多個key
但是一個key只能對應一個value
例如常用的是用 int 將 string 做編號 :
map<int, string> m;
int n;
string s;
cin >> n >> s;
m[n] = s;
//Beware of the input order must suit the format of map而欲讀取資料的話需給予他iterator
注意:如果使用iterator時要符合格式.如果有格式不同的map則需另建一個新的iterator不可共用
map在資料存取中.key的為.first, value的為.second
例如要讀取所有的map的資料
(.begin
cout << "The datas stored in the map are: ";
for(it = m.begin(); it!= m.end(); it++)
{
cout << (*it).first << " " << (*it).second << endl;
}
//.begin() stands for the first data stored in the map或是如果只有要讀取“被你編號的某個” string
int search;
cout << "Input the number ID of the string you are looking for : ";
cin >> search;
cout << m[search] << endl;An fully executable program example :
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
map<int, string> m;
map<int, string>::iterator it;
int n;
string s;
int search;
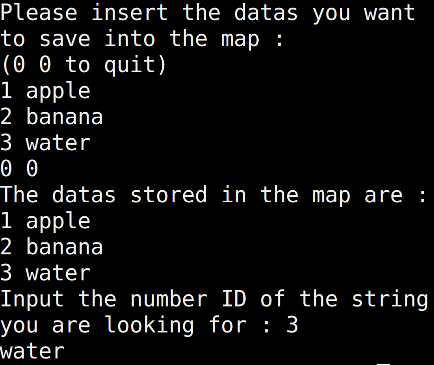
cout << "Please insert the datas you want to save into the map :" << endl;
cout << "(0 0 to quit)" << endl;
while(1)
{
cin >> n >> s;
if(n == 0 && s == "0")
break;
m[n] = s;
}
cout << "The datas stored in the map are : " << endl;
for(it = m.begin(); it!= m.end(); it++)
{
cout << (*it).first << " " << (*it).second << endl;
}
cout << "Input the number ID of the string you are looking for : ";
cin >> search;
cout << m[search] << endl;
}Output:
Member functions
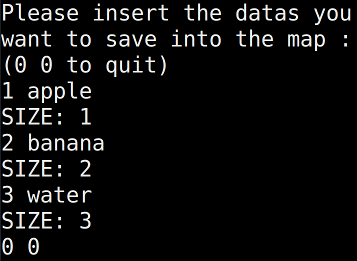
.size()
可以用來檢測當前map裡有幾筆資料
例如
map<int, string> m;
int n;
string s;
while(1)
{
cin >> n >> s;
if(n == 0 && s == "0")
break;
m[n] = s;
cout << "SIZE: " << m.size() << endl;
}
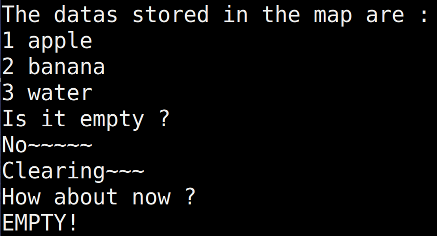
.clear() / .empty()
.clear()是用來清空map裡所有資料的一個member function
.empty()是用來察看map裡的資料是否是空的的member function (returns boolean)
cout << "Is it empty ?" << endl;
if(m.empty())
cout << "Yes~" << endl;
else
cout << "No~~~~~" << endl;
cout << "Is it empty now?" << endl;
m.clear();
if(m.empty())
cout << "EMPTY!" << endl;
else
cout << "Nope" << endl;