ChibiOS/RT
組員
- 莊承翰 / vchchuang
- 詹尚倫 / game
- 陳祐任 / bruce30262
- 陳易駿 / alex122380
- 郭耀琮 / rbugoo131
共筆: hackpad
ChibiOS/RT 參考應用
測試環境架設
安裝 neocon wget http://svn.openmoko.org/developers/werner/neocon/Makefile
wget http://svn.openmoko.org/developers/werner/neocon/neocon.c
make
cp neocon /usr/bin
燒錄ChibiOS/RT,參考 ChbiOSRT
run testsuite 輸入 neocon /dev/ttyUSB0 會看到以下畫面
接著按下 Enter 後,會見當畫面如下
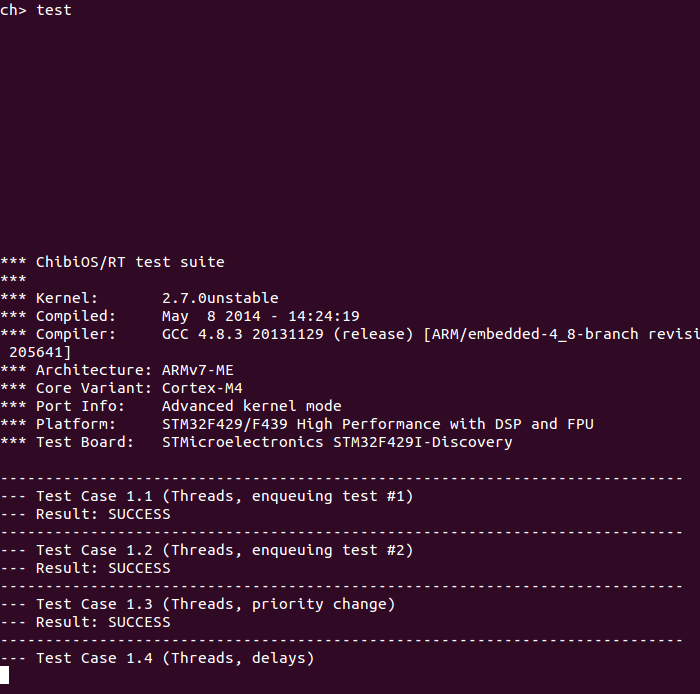
輸入 test 後會看到test suite的結果
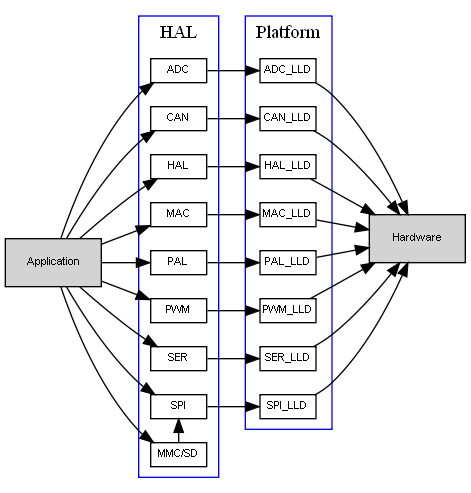
作業系統架構
ChibiOS/RT 是一個相當模組化的設計,部由許多主要的獨立組件構成。而每一個組件又可能細分成許多子系統

kernel : OS kernel中與平台無關的部份
port layer :OS kernel中與結構/編譯器 相關的部份
HAL(hardware abstraction layer) : 包含許多抽象的device drivers,提供普遍的I/O API給不同平台的應用程式
platform layer : 包含許多device drivers的實作
various : 提供各種額外但不包含在特定組件的工具的函式庫
HAL 與 platform關係如下
系統狀態(System States) ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^



- Init
- ChibiOS/RT 進行OS初始化之前的狀態,進行所謂的物理重置(physical reset)時也會進到這個狀態
- 呼叫chSysInit()這個函式進行初始化
- 在這個狀態裡所有可以發出Maskable Interrupt的sources全部失效
- 初始化完後進到 Normal
- Normal
- 初始化完後到達的狀態
- 在這裡可以執行Thread, 接收並處理任何中斷及呼叫任何system API
- Suspended
- 在這個狀態裡,無法接收正常中斷(IRQ),但是可以接收快速中斷(FIQ)
- 除了可以呼叫chSysDisable()到達Disable狀態,以及chSysEnable()到達Normal狀態之外,其他所有system API都不能呼叫
- Disabled
- 所有可遮罩式中斷資源全部失效,系統僅能處理不可遮罩式中斷(NMI)
- 除了可以呼叫chSysEnable()到達Normal狀態,以及chSysSuspend()到達Suspended狀態之外,其他所有system API都不能呼叫
- Sleep
- 當系統中沒有其他的Thread要跑時,此時系統會執行一個 idle thread,到達這個狀態
- 此時系統將處於 low power mode,並等待一個中斷跳出這個狀態
- 接收到一個IRQ時,將會跑到 SRI 狀態去處理中斷,處理完後會回到 Normal
- S-Locked
- 在 Normal 的狀態中呼叫 chSysLock() 之後會進入此狀態
- 此時系統會進入 Kernel locked 的狀態
- 此時處理器會跑在 thread-privileged mode
- 在這個狀態裡,無法接收正常中斷(IRQ),但是可以接收快速中斷(FIQ)
- 在這個狀態裡可以使用 S class 和 I class 的 API
- 呼叫 chSysUnlock() 會回到 Normal 狀態
- 在 Normal 的狀態中呼叫 chSysLock() 之後會進入此狀態
- I-Locked
- 在 SRI 的狀態中呼叫 chSysLockFromIsr() 之後會進入這個狀態
- 此時系統會進入 Kernel locked 的狀態
- 此時處理器會跑在 exception-privileged mode
- 在這個狀態裡,無法接收正常中斷(IRQ),但是可以接收快速中斷(FIQ)
- 在這個狀態裡可以使用 I class 的 API
- 呼叫 chSysUnlockFromIsr() 會回到 SRI 狀態
- Serving Regular Interrupt ( SRI )
- 處理一個正常中斷 ( IRQ ) 時,會進入這個狀態
- 此時只有更高等級的中斷能夠進行搶佔
- 此時處理器會跑在 exception-privileged mode
- 此時無法呼叫大部分的 system API,除非先呼叫 chSysLockFromIsr() 進入 I-Locked state,之後才能夠進行其他 API 的呼叫
- Serving Fast Interrupt ( SFI )
- 處理一個快速中斷 ( FIQ ) 時會進入這個狀態
- 無法呼叫所有 system API
- 除了 Init , Halted , SNMI , Disabled 之外的任一狀態,只要接收到 FIQ 就會跳到這個狀態,處理完後會回到上一狀態
- Serving Non-Maskable Interrupt ( SNMI )
- 處裡一個不可遮罩式的中斷時 (NMI) 會進入這個狀態
- 無法呼叫所有 system API
- 除了 Halted 的任一狀態裡只要接收到 NMI,或是在 Halted 中收到非同步的 NMI 時就會跳到這個狀態,處理完後會回到上一狀態
- Halted
- 呼叫 chSysHalt() 時會進入這個狀態
- 所有中斷都不能使用
中斷(Interrupt) ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ * 先備知識 + 可遮罩式中斷 ( Maskable
Interrupt ) :
- 一種硬體中斷 - 可以透過軟體控制去設定中斷遮罩暫存器 ( Interrupt Mask
Register ) 內的位元遮罩值 ( bit-mask )
來讓CPU決定要不要回應這個中斷要求。 + 不可遮罩式中斷 ( Non-Maskable
Interrupt, NMI ) :
- 一種硬體中斷 -
與可遮罩式中斷不同,它無法用軟體去控制。CPU一定要回應這個中斷要求,不可以忽略。
+ 中斷遮罩暫存器 ( Interrupt Mask Registers ) : 在 ARM
Cortex-M3中,可以透過設定中斷遮罩暫存器,來控制系統的中斷。共有三種: -
PRIMASK : 一個只有一個 bit 的暫存器。設為1時,系統將只會處理 NMI 和 hard
fault
exception,其他可遮罩式中斷將被全部忽略。設為0時,則可以處理所有中斷。 -
FAULTMASK: 一個只有一個 bit 的暫存器。設為1時,系統將只會處理
NMI,其他像是 hard fault exception
或是可遮罩式中斷都將被全部忽略。設為0時,則可以處理 hard fault
exception。 - BASEPRI: 8個 bit 的暫存器,用來儲存優先度等級( priority
level
)。當這個暫存器被設為一個非0值時,系統將會忽略優先度比這個值還要大(代表優先度等級較低)
的中斷。
- Chibi OS/RT 的中斷類別
- 正常中斷 ( Regular Interrupts ):
- 可遮罩式的中斷
- 在 GCC Ports / ARM Cortex-Mx / ARMv7-M 的移植版本中,優先度等級較低的中斷將被視為正常中斷
- 無法搶佔部分的 kernel code
- 在此類的 interrupt handler 裡面可以呼叫 operating system APIs。
- 快速中斷 ( Fast Interrupts ):
- 可遮罩式的中斷
- 在 GCC Ports / ARM Cortex-Mx / ARMv7-M 的移植版本中,優先度等級較高的中斷將被視為快速中斷
- 可以搶佔 kernel code ,也因此有較短的延遲 ( lantency ) 。
- 在此類的 interrupt handler 裡面無法呼叫任何一個 operating system API 。
- 不可遮罩式中斷 ( Non Maskable Interrupts, NMI):
- 不受OS控制的中斷,擁有最短的延遲 ( lowest latency )
- 正常中斷 ( Regular Interrupts ):
- Chibi OS/RT 中對 STM32F4XX 系列所支援的中斷
- 共定義了99種中斷
- hal_lld.h 中定義了可用的 ISR name 和 對應的 vector name
- 而在 /os/ports/GCC/ARMCMx/STM32F4xx/vectors.c 中則定義了 Interrupt Vector Table 及宣告了處理 Interrupt 的函式
- 另外在 /os/hal/platforms/STM32F4xx/stm32f4xx.h 中有一段 code 定義了 Interrupt number
- 如何設定中斷
- 中斷的初始設定
- 根據所要設定的中斷,確定其 ISR name 和 interrupt number
- 如果為自設的外部中斷 ( external interrupt, EXTI ) :
- 則還要先設定 GPIO
- 最後要記得呼叫 NVICEnableVector( Interrupt_Number, Interrupt_priority ) 這個函式,將這個 external interrupt 做 enabled 的動作
- 設定其 priority ( 注意 IRQ 的 priority 不能設太高 )
- 撰寫 Interrupt Handler
需依照規定的格式撰寫
.. code-block:: c
CH_IRQ_HANDLER(ISR_name) // 傳入參數為一 ISR name { CH_IRQ_PROLOGUE();
/* IRQ handling code, preemptable if the architecture supports it.*/ chSysLockFromIsr(); /* Invocation of some I-Class system APIs, never preemptable.*/ chSysUnlockFromIsr(); /* More IRQ handling code, again preemptable.*/ CH_IRQ_EPILOGUE();}
如果為快速中斷 ( FIQ ) 則不需要 prologue/epilogue,也不能夠呼叫 API
.. code-block:: c
CH_FAST_IRQ_HANDLER(myIRQ) { /* Fast IRQ handling code, preemptable if the architecture supports it. The invocation of any API is forbidden here because fast interrupt handlers can preempt the kernel even within its critical zones in order to minimize latency.*/ }
- 中斷的初始設定
執行緒(Thread)狀態 ^^^^^^^^^^^^^
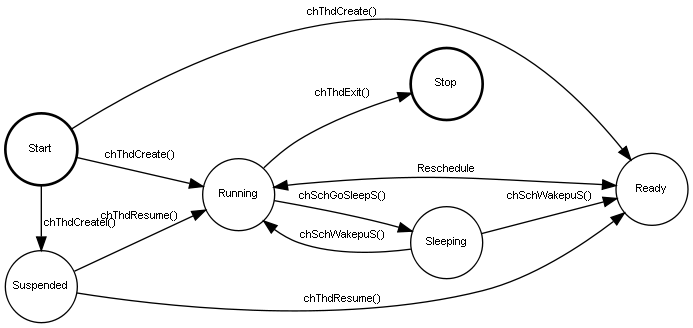
- Start : 初始的狀態
- Suspended : Thread剛被create出來時的狀態,尚未決定要被放進ReadyList等待執行或是直接執行
- Running : 正在執行中的狀態
- Stop : 終止的狀態,到達這個狀態表示Thread被執行完了
- Sleeping : Thread暫時不進行工作。此時Thread會被暫時移出ReadyList。等待Mutex解鎖,等待其他Thread執行完,或是等待接收訊息時都會進入這個狀態。
- Ready : 被放進ReadyList, 等待被執行的狀態
ChbiOS/RT 初始化後會建立兩個 thread + Idle thread : - priority level最低,只有在其他thread 處於sleep狀態時才會執行,通常在執行這個threaad時 系統會進入low power mode 且不會做任何事情 + Main thread : - priority=NORMALPRIO ,此thread在一開始執行main() function,且需要時可以變更自己的priority,通常其他的thread也都是由此建立的
Thread and Structure Reference ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ 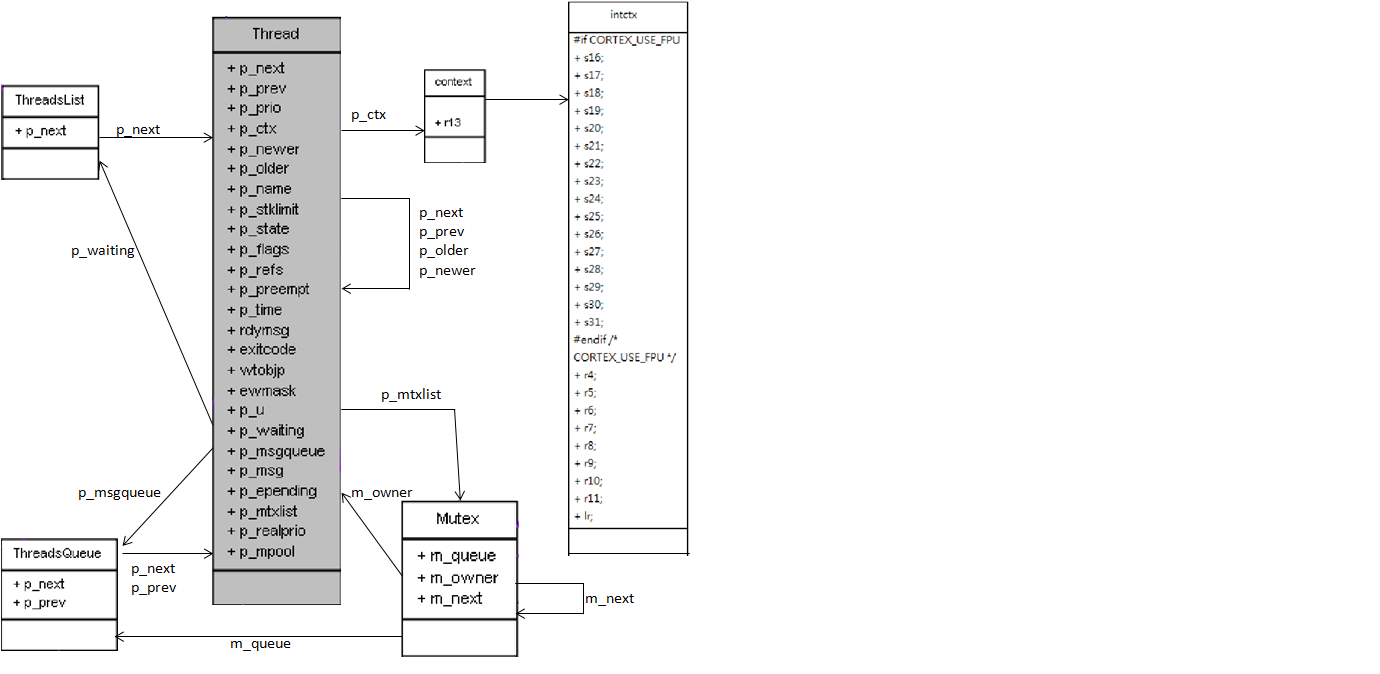
- 較重要的 member data
- p_prio : Thread priority
- p_ctx : Processor context, 紀錄 Thread 目前的執行狀態
- p_state : 紀錄 Thread 目前所處於的狀態 (正在執行, 等待被執行, 等待某一個 Mutex 被解鎖….等)
- p_preempt : 記錄這個 Thread 還有多少個 tick 可以用來執行
- p_waiting : 一個單向的 Thread linked list。 當有其他 Thread 欲等待此 Thread 執行完時, 這些 Thread 就會被塞進這個 waiting list 裡面
- p_msgqueue : 一個雙向的 Thread linked list。 用來存放欲傳給此 Thread 訊息的 Thread (詳見後面 IPC 的部分)。
- p_mtxlist : Mutex 結構,用來存放此 Thread 目前佔有的 Mutex
Creating Thread ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ | ChibiOS 有 2 種創造 Thread 的方式: 靜態 ( static ) 和動態 ( dynamic)
- 靜態
- 首先利用 WORKING_AREA(Thread_Name, stack_size) 這個 macro
去配置一塊記憶體給 Thread
- 包括這條 Thread 所需要的 stack memory , Thread 自己本身存 stucture data 用的 memory
- 還有 external context, internal context (詳見後面 context switch 的部分)和 interrupt stack(用來 serve interrupt 用的)
- 接著呼叫 chThdCreateStatic() 來創造一個靜態的 Thread
- chThdCreateStatic () 裡面會呼叫到一行 chSchWakeupS(tp =
chThdCreateI(wsp, size, prio, pf, arg), RDY_OK);
- chThdCreateI() 會將這個 Thread 的資料結構做好初始化 (包括設定好 priority, 初始的 function pointer…等等)
- chSchWakeupS() 則是會比對新建的 Thread, 與目前的 Thread 哪個 priority 比較高, 並決定新建的 Thread 是可以立刻開始跑或是要被放入 ready list。
- 首先利用 WORKING_AREA(Thread_Name, stack_size) 這個 macro
去配置一塊記憶體給 Thread
- 動態
- 可利用 chThdCreateFromHeap() 或是 chThdCreateFromMemoryPool() 來動態新增 Thread
- From heap:
- 從Heap中動態配置一塊記憶體
- Create 時間不固定,但宣告的working area 大小是彈性的 (相同大小的記憶體下 memory pool 較快,1/2倍左右)
- 相當於malloc & free
- Heap 易存在 memory fragmentation 的問題
- 需要針對每一個thread release,需要多次操作
- From memory heap
- 從Memory pool 中動態配置一塊記憶體
- Create時間固定,宣告的working area 大小是固定的 (相同大小->THREAD_STACK_SIZE 下,比heap快,2倍左右)
- 不易存在memory fragmentation 的問題
- 可直接release memory pool,一次操作就好
- 動態 Thread 的釋放 : chThdRelease()
- 會先查看 Thread 有無執行完,且是否還有其他 Thread 指向這塊記憶體
- Thread 的狀態是執行完且沒有其他 Thread 指向這塊記憶體的話就進行釋放記憶體的動作
行程間通訊 ( Inter-Process Communication, IPC ) ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ * Semaphore + Counting Semaphore - .. code-block:: c
typedef struct Semaphore
{
ThreadsQueue s_queue; /**< @brief Queue of the threads sleeping on this semaphore. */
cnt_t s_cnt; /**< @brief The semaphore counter. */
} Semaphore;
- 呼叫 chSemWaitS() 來等待,取用 Semaphore
- 如果沒有 semaphore 可以取用則進入 s_queue 裡面等待
- 呼叫 chSemSignalI() 來釋放 Semaphore
- 釋放後會先看 s_queue 裡面有沒有 Thread 在等待,有的話就 pop 一條 Thread 出來給他用
+ Binary Semaphore
- 直接採用 Counting Semaphore 的方式實作 Binary Semaphore
- Counter 被限制為不能超過 1
- 一個 Binary Semaphore 不能重複做 signal 運算- Mutex
.. code-block:: c
typedef struct Mutex { ThreadsQueue m_queue; /**< @brief Queue of the threads sleeping on this Mutex. */ Thread *m_owner; /**< @brief Owner @p Thread pointer or @p NULL. */ struct Mutex *m_next; /**< @brief Next @p Mutex into an owner-list or @p NULL. */ } Mutex;實作 Mutex (假設有 Thread A 欲鎖住一個 Mutex)
- 先判斷這個 Mutex 有無其他 Thread 鎖著
- 沒有的話就直接鎖住
- 有的話會再判斷鎖住這個 Mutex 的 Thread ( 假設為Thread B ), 它的 priority 有沒有比 Thread A 大
- 如果比 Thread A 大, 則 Thread A 會按照其 priority 被塞進這個 Mutex 的 m_queue 裡, 與其他 Thread 一起等待這個 Mutex 被解鎖
- 如果比 Thread A 小, 則會先將 Thread B 的 priority 提升至跟 Thread A 一樣的 level, 並做 Reschedule 的動作,讓 Thread B 快點執行完。至於 Thread A 則會按照其 priority 被塞進這個 Mutex 的 m_queue 裡, 與其他 Thread 一起等待這個 Mutex 被解鎖。
- Synchronous Messages
在 ChibiOS / RT 之中,Thread 與 Thread 之間也有所謂的同步訊息傳送/接收機制
傳送者 ( Sender )
- 呼叫 chMsgSend() 來傳送訊息
- 此時會被塞進接收者的 p_msgqueue 裡面(等待接收者提取訊息)
- 判斷接收者的狀態,並喚醒接收者,告知訊息已傳送,可以起來接收訊息了
- 傳送者自己本身會進入某種睡眠狀態 ( THD_STATE_SNDMSGQ )
- 接收者收到訊息後,會呼叫 chMsgRelease() 喚醒傳送者,告知訊息傳遞已經結束,可以起來了
接收者 ( Reciever )
- 呼叫 chMsgWait() 來等待接收訊息
- 此時會先進入某種睡眠狀態 ( THD_STATE_WTMSG )
- 直到被傳送者喚醒後,會從自己的 p_msgqueue 裡面提取訊息接收
- 最後把傳送者的狀態設成 ( THD_STATE_SNDMSG ),並呼叫 chMsgRelease()喚醒傳送者,告知訊息傳遞已經結束,可以起來了
Receiver
.. code-block:: c
static msg_t thread1(void *p) { Thread *tp; msg_t msg; (void)p; do { tp = chMsgWait(); msg = chMsgGet(tp); chMsgRelease(tp, msg); } while (msg); return 0; }Sender
.. code-block:: c
static unsigned int msg_loop_test(Thread *tp) {
uint32_t n = 0; test_wait_tick(); test_start_timer(1000); do { (void)chMsgSend(tp, 1); n++; } while (!test_timer_done); (void)chMsgSend(tp, 0); return n;}
How to use
.. code-block:: c
threads[0] = chThdCreateStatic(wa[0], WA_SIZE, chThdGetPriority()+1, thread1, NULL); n = msg_loop_test(threads[0]);
Ready List ^^^^^^^^^^^^^ ChibiOS/RT 的 ready list以doubly linked list 實作
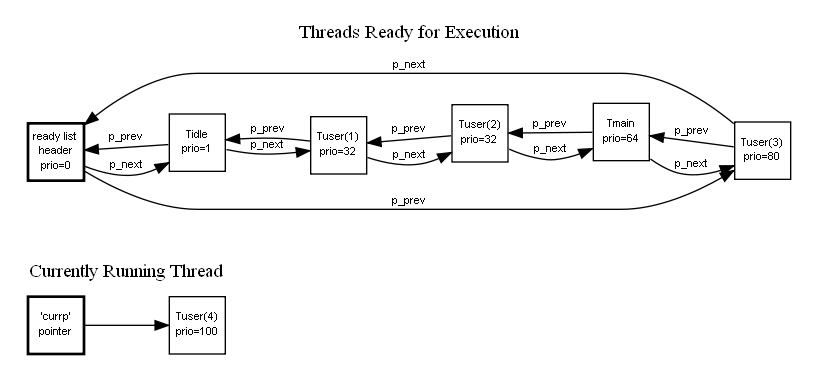
數字愈大,優先權愈大 ( priority 相同的話,採用 round-robin strategy)
- 執行序的priority level
- IDLEPRIO :
- value = 1
- 保留給Idle Thread的特殊priority level
- LOWPRIO :
- value = 2
- user thread 中 priority level 最低
- NORMALPRIO :
- value = 64
- main() thread從這個level開始,通常user thread 的priority level是以此為中心
- HIGHPRIO :
- value = 127
- user thread 中 priority level 最高
- IDLEPRIO :
選出下一個可執行的thread, 並進行Context Switch
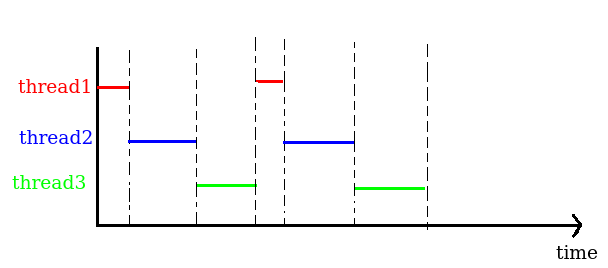
priority較低的thread會被priority較高的thread preempt,並重置其p_preept值為CH_TIME_QUANTUM
priority相同的話,thread擁有CH_TIME_QUANTUM 時間的CPU控制權,如果用完了就會必須切換到下一個thread
Round Robin scheduling
執行中的thread 自主性地呼叫chThdYield() API,讓其他相同priority的thread來執行
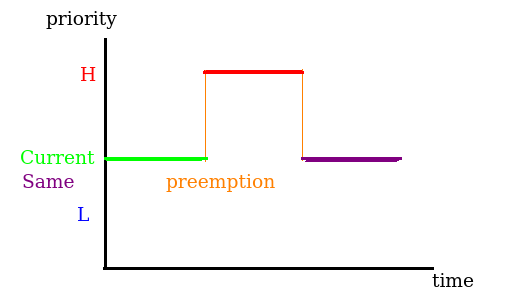
執行中的thread 自主性地進入sleep mode且當有thread被wake up時,執行中的thread 就會被中斷並插入其他任意一個相
同priority thread的後面執行中的thread被擁有更高priority的thread preempted,那麼執行中的thread 就會被中斷並插入其他任意一個相同priority thread的後面
如果thread 的執行時間超過 CH_TIME_QUANTUM (大於0)且有相同priority的thread在ready list中的話,那麼執行中的thread 就會被中斷並插入其他任意一個相同priority thread的後面
與一般RR不同的地方是其為 preemptive RR
內文切換(Context Switch) ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
extctx {r0-r3, r12, lr_thd, pc, xpsr}
intctx {r4-r11, lr}
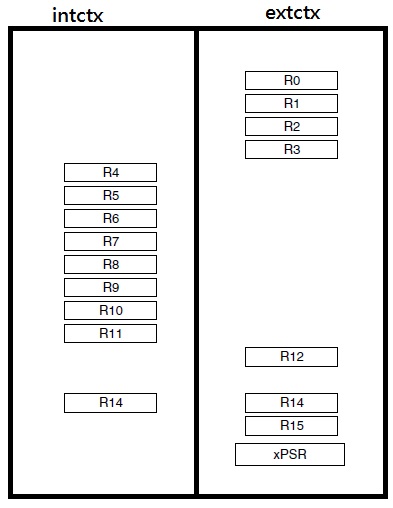
分別是發生interrupt時會被自動存起來的extctx(external context),和程式內部在執行context switch時會存起來的intctx(interanl context)。
每當一個準備離開一個interrupt時,會執行一段IRQ_EPILOGUE(),IRQ_EPILOGUE()當中會push一個artificial exception return context,讓離開interrupt
unstacking的時候,pc會指向port_switch_from_isr()或是port_exit_from_isr()。
每一個thread被切換回來的時候,會再呼叫svc call來將artificial exception return context丟掉並取回原本的extctx。
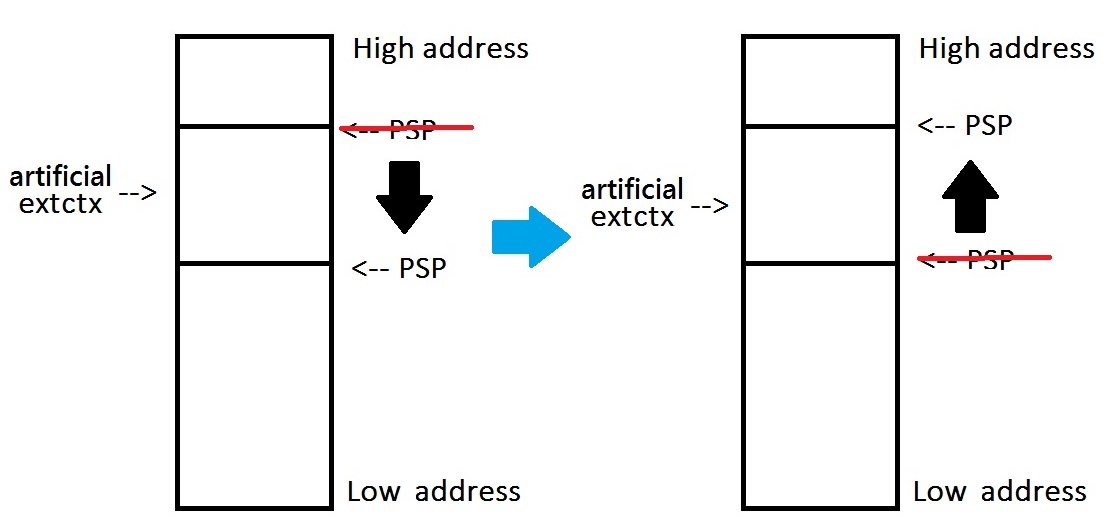
_port_irq_epilogue()
.. code-block:: c
void _port_irq_epilogue(void) {
port_lock_from_isr();
if ((SCB_ICSR & ICSR_RETTOBASE) != 0) { //there are no active exceptions, or the currently-executing exception is the only active exception.
struct extctx *ctxp;
/* Current PSP value.*/
asm volatile ("mrs %0, PSP" : "=r" (ctxp) : : "memory");
/* Adding an artificial exception return context, there is no need to
populate it fully.*/
ctxp--;
asm volatile ("msr PSP, %0" : : "r" (ctxp) : "memory");
ctxp->xpsr = (regarm_t)0x01000000;
/* The exit sequence is different depending on if a preemption is
required or not.*/
if (chSchIsPreemptionRequired()) {
/* Preemption is required we need to enforce a context switch.*/
ctxp->pc = (void *)_port_switch_from_isr;
#if CORTEX_USE_FPU
/* Triggering a lazy FPU state save.*/
asm volatile ("vmrs APSR_nzcv, FPSCR" : : : "memory");
#endif
}
else {
/* Preemption not required, we just need to exit the exception
atomically.*/
ctxp->pc = (void *)_port_exit_from_isr;
}
#if CORTEX_USE_FPU
{
uint32_t fpccr;
/* Saving the special register SCB_FPCCR into the reserved offset of
the Cortex-M4 exception frame.*/
(ctxp + 1)->fpccr = (regarm_t)(fpccr = SCB_FPCCR);
/* Now the FPCCR is modified in order to not restore the FPU status
from the artificial return context.*/
SCB_FPCCR = fpccr | FPCCR_LSPACT;
}
#endif
/* Note, returning without unlocking is intentional, this is done in
order to keep the rest of the context switch atomic.*/
return;
}
port_unlock_from_isr();
}.. code-block:: c
void _port_switch_from_isr(void) {
dbg_check_lock();
chSchDoReschedule();
dbg_check_unlock();
asm volatile ("_port_exit_from_isr:" : : : "memory");
#if !CORTEX_SIMPLIFIED_PRIORITY || defined(__DOXYGEN__)
asm volatile ("svc #0");
#else /* CORTEX_SIMPLIFIED_PRIORITY */
SCB_ICSR = ICSR_PENDSVSET;
port_unlock();
while (TRUE)
;
#endif /* CORTEX_SIMPLIFIED_PRIORITY */
}.. code-block:: c
void chSchDoReschedule(void) {
#if CH_TIME_QUANTUM > 0 /* If CH_TIME_QUANTUM is enabled then there are two different scenarios to handle on preemption: time quantum elapsed or not./ if (currp->p_preempt == 0) { / The thread consumed its time quantum so it is enqueued behind threads with same priority level, however, it acquires a new time quantum./ chSchDoRescheduleBehind(); } else { / The thread didn’t consume all its time quantum so it is put ahead of threads with equal priority and does not acquire a new time quantum./ chSchDoRescheduleAhead(); } #else / !(CH_TIME_QUANTUM > 0) / / If the round-robin mechanism is disabled then the thread goes always ahead of its peers./ chSchDoRescheduleAhead(); #endif / !(CH_TIME_QUANTUM > 0) */ }
.. code-block:: c
void SVCallVector(void) {
struct extctx *ctxp;
/* Current PSP value.*/
asm volatile ("mrs %0, PSP" : "=r" (ctxp) : : "memory");
/* Discarding the current exception context and positioning the stack to
point to the real one.*/
ctxp++;
#if CORTEX_USE_FPU
/* Restoring the special register SCB_FPCCR.*/
SCB_FPCCR = (uint32_t)ctxp->fpccr;
SCB_FPCAR = SCB_FPCAR + sizeof (struct extctx);
#endif
asm volatile ("msr PSP, %0" : : "r" (ctxp) : "memory");
port_unlock_from_isr();
}.. code-block:: c
void _port_switch(Thread *ntp, Thread *otp) {
asm volatile ("push {r4, r5, r6, r7, r8, r9, r10, r11, lr}" ←儲存舊的thread的狀態
: : : "memory");
#if CORTEX_USE_FPU
asm volatile ("vpush {s16-s31}" : : : "memory");
#endif
asm volatile ("str sp, [%1, #12] \n\t" ←切換stack pointer所指的位址
"ldr sp, [%0, #12]" : : "r" (ntp), "r" (otp)); ←
#if CORTEX_USE_FPU
asm volatile ("vpop {s16-s31}" : : : "memory");
#endif
asm volatile ("pop {r4, r5, r6, r7, r8, r9, r10, r11, pc}" ←讀入新的thread的狀態
: : : "memory");
}硬體驅動原理
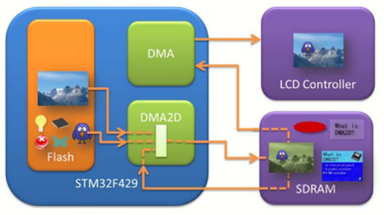
以 DMA2D 為例
DMA2D的架構簡圖:
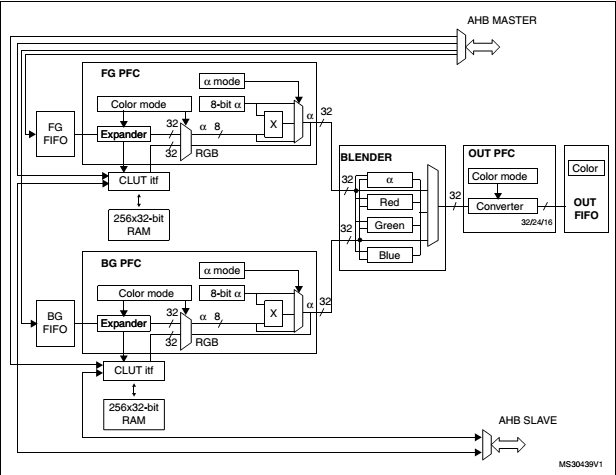
在對硬體的driver作設計時會用到很多_IO的type
在core_cm4.h裡找到相關定義 .. code-block:: c
#define __IO volatile /!< Defines ‘read / write’ permissions/
DMA2D的流程簡圖:
DMA2D memory address
- 記錄在stm32f4xx.h
- 記憶體區間在:0x4002 B000 - 0x4002 BBFF reference
.. code-block:: c
#define PERIPH_BASE ((uint32_t)0x40000000) /!< Peripheral base address in the alias region #define AHB1PERIPH_BASE (PERIPH_BASE + 0x00020000) #define DMA2D_BASE (AHB1PERIPH_BASE + 0xB000) #define DMA2D ((DMA2D_TypeDef )DMA2D_BASE)
- 設定要取得的資料
.. code-block:: c
static uint8_t frame_buffer[240 * 320 * 3] attribute((section(“.sdram”)));
- DMA2D的JOB模式
.. code-block:: c
#define DMA2D_JOB_COPY (0 << 16) /**< Copy, replace(FG only).*/ #define DMA2D_JOB_CONVERT (1 << 16) /**< Copy, convert (FG + PFC).*/ #define DMA2D_JOB_BLEND (2 << 16) /**< Copy, blend (FG + BG + PFC).*/ #define DMA2D_JOB_CONST (3 << 16) /**< Default color only (FG REG).*/
DMA2D的API與資料結構設定,記錄在stm32_dma2d
- dma2d_layercfg_t的struct
========== ==== ================ ==== =============== Type Name
Description
————————————————————- void bufferp Frame buffer address size_t
wrap_offset Offset between lines, in pixels dma2d_pixfmt_t fmt Pixel
format dma2d_color_t def_color Default color, RGB-888 uint8_t
const_alpha Constant alpha factor dma2d_palcfg_t palettep Palette
specs, or @p NULL
========== ==== ================ ==== ===============
- DMA2D TypeDef:
============== === ================================================ == ===================== Name Description Address offset ———————————————————————————————— CR Control Register 0x00 ISR Interrupt Status Register 0x04 IFCR Interrupt Flag Clear Register 0x08 FGMAR Foreground Memory Address Register 0x0C FGOR Foreground Offset Register 0x10 BGMAR Background Memory Address Register 0x14 BGOR Background Offset Register 0x18 FGPFCCR Foreground PFC Control Register 0x1C FGCOLR Foreground Color Register 0x20 BGPFCCR Background PFC Control Register 0x24 BGCOLR Background Color Register 0x28 FGCMAR Foreground CLUT Memory Address Register 0x2C BGCMAR Background CLUT Memory Address Register 0x30 OPFCCR Output PFC Control Register 0x34 OCOLR Output Color Register 0x38 OMAR Output Memory Address Register 0x3C OOR Output Offset Register 0x40 NLR Number of Line Register 0x44 LWR Line Watermark Register 0x48 AMTCR AHB Master Timer Configuration Register 0x4C RESERVED[236] Reserved 0x50-0x3FF FGCLUT[256] Foreground CLUT 400-7FF BGCLUT[256] Background CLUT 800-BFF ============== === ================================================ == =====================
效能表現
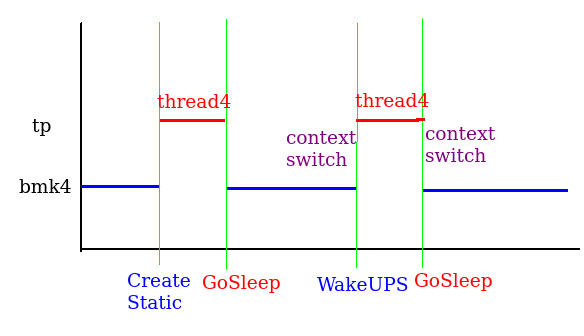
- context switch
Sleep and Wakeup context switch的次數 610928 ctxswc/S =>610928次/秒 = 1.63 us/次 .. code-block:: c
test_wait_tick(); test_start_timer(1000); do { chSysLock(); chSchWakeupS(tp, RDY_OK); chSchWakeupS(tp, RDY_OK); chSchWakeupS(tp, RDY_OK); chSchWakeupS(tp, RDY_OK); chSysUnlock(); n += 4; } while (!test_timer_done);在時間內每次iteration作四次的Wakeup的動作,最後乘以二
Message send and receive
* Receiver .. code-block:: c static msg_t thread1(void *p) { Thread *tp; msg_t msg; (void)p; do { tp = chMsgWait(); msg = chMsgGet(tp); chMsgRelease(tp, msg); } while (msg); return 0; } * Sender .. code-block:: c static unsigned int msg_loop_test(Thread *tp) { uint32_t n = 0; test_wait_tick(); test_start_timer(1000); do { (void)chMsgSend(tp, 1); n++; #if defined(SIMULATOR) ChkIntSources(); #endif } while (!test_timer_done); (void)chMsgSend(tp, 0); return n; } 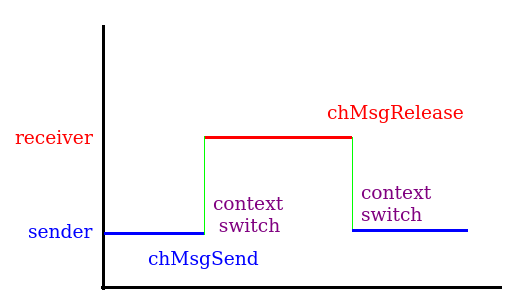 - 情況1: Send priority 比 Receive priority 高(Test Case 11.1) context switch的次數 341088 ctxswc/S =>341088 次/秒 = 2.93 us/次 - 情況2: Send priority 比 Receive priority 低(Test Case 11.2) context switch的次數 274588 ctxswc/S =>274588 次/秒 = 3.64 us/次
Q & A:
Q1:S Lock & I Lock作法的優點和缺點?對OS有何幫助?
A:
- S lock 與 I lock同屬於kernel lock ,實作上會將Interrupt關閉 ,S-class與I-class API只能在kernel lock狀態下使用 ,而兩者不同在於S-class 不能被ISR使用而I-class可以。
- 因為S-class會在內部做reschedule或者會涉及到當前thread而且ISR不被允許使用reschedule。
- 由於ISR結束後會自動做reschedule ,如果ISR中涉及到當前thread這沒有意義因為ISR可能已preempt某個thread。
舉例 :Init -> Normal
-狀況一:(Normal —–> S-state —-context_switch—–> I-state —-context_switch—–> S-state —–> Normal)
.. code-block:: c
Main thread -> chThdCreateStatic(waThread1, sizeof(waThread1), NORMALPRIO + 10,Thread1, NULL); ->chSysLock() <-使系統進到S狀態 ->chSchWakeupS(tp = chThdCreateI(wsp, size, prio, pf, arg), RDY_OK); if(Thread1 優先程度 不大於 當前thread) 是做->chSchReadyI(ntp) <-做schdule 否做->chSysSwitch(ntp, otp) <- 資源主動switch給ntp ,系統狀態S至I ->chSysUnlock() <- ntp被switch離開 系統狀態 I 至 S ,資源給chSysUnlock執行結束後系統回到Normal 狀態-狀況二:(Normal -> SRI -> I-state )
Q2:找出Thread SLEEP條件。
A: 等待message , mutex解鎖, 等待另外一條thread執行完…等等, 都會進入sleep state (sleep state中又定義許多不同的state)
Q3:msg_queue & thread_queue 關聯在哪?用法? List & Queue 用途?
A: ThreadQueue因為是採用priority_insert的方式,所以用double linked list實作效率會比較高 (code)
Q4:Binary Semaphore 與mutex 本質上有什麼不同?
A: 最主要還是在於ownership。mutex有ownership的概念,semaphore沒有所以如果一個thread要取用一個semaphore的話你就給我進threadQueue裡面等到有空的semaphore給你用你才能用。mutex則不同,因為有ownership的概念所以可以透過尋找占用此mutex的thread,來決定說需不需要做提升priority的動作,也因此mutex不會有priority inversion的情形發生(semaphore就會)。
Q5:context switch效能測試算法中為何在取得時間前要做乘2動作?
A: 因為
Q6:Create thread from heap v.s. mem pool的時間複雜度為何(bigO)?
A: Heap is O(n) ,根據實驗所做之圖:
Q7:mutex與semephore(binary)為何在同時間內的lock與unlock次數不同?
A:因為mutex會有priority inversion的可能,所以會較semaphore慢(1.mutex v.s semaphore 2. chibios)
in code priority inversion 的實作:
.. code-block:: c
while (tp->p_prio < ctp->p_prio) { /* Make priority of thread tp match the running thread's priority.*/ tp->p_prio = ctp->p_prio; /* The following states need priority queues reordering.*/ switch (tp->p_state) { case THD_STATE_WTMTX: /* Re-enqueues the mutex owner with its new priority.*/ prio_insert(dequeue(tp), (ThreadsQueue *)tp->p_u.wtobjp); tp = ((Mutex *)tp->p_u.wtobjp)->m_owner; continue; #if CH_USE_CONDVARS | \ (CH_USE_SEMAPHORES && CH_USE_SEMAPHORES_PRIORITY) | \ (CH_USE_MESSAGES && CH_USE_MESSAGES_PRIORITY) #if CH_USE_CONDVARS case THD_STATE_WTCOND: #endif #if CH_USE_SEMAPHORES && CH_USE_SEMAPHORES_PRIORITY case THD_STATE_WTSEM: #endif #if CH_USE_MESSAGES && CH_USE_MESSAGES_PRIORITY case THD_STATE_SNDMSGQ: #endif /* Re-enqueues tp with its new priority on the queue.*/ prio_insert(dequeue(tp), (ThreadsQueue *)tp->p_u.wtobjp); break; #endif case THD_STATE_READY: #if CH_DBG_ENABLE_ASSERTS /* Prevents an assertion in chSchReadyI().*/ tp->p_state = THD_STATE_CURRENT; #endif /* Re-enqueues tp with its new priority on the ready list.*/ chSchReadyI(dequeue(tp)); break; } break; }
