版本 6ae0ede0ed312329a54138237acb1978d309a043
nuttx
組員
- 翁振育
- 黃亮穎
- 蘇偉嘉
- 李英碩
github : https://github.com/gototop/nuttx-stm32f4disc-bb
Nuttx 參考應用
NuttX 架構
與平台相關
Run Nuttx on STM32F429-Disco
(2) cd workspace/nuttx-stm32f4disc-bb/nuttx/tools
(3) ./configure.sh stm32f429i-disco/nsh
(4) cd ..
(5) make CROSSDEV=arm-none-eabi-
(6) st-flash write nuttx.bin 0x8000000
(7) sudo screen /dev/ttyUSB0 115200 8n1
設定相關應用程式與功能
120 CONFIG_ARCH_FPU=n
465 CONFIG_RTC=y
466 CONFIG_RTC_DATETIME=y
653 CONFIG_EXAMPLES_HELLO=y
676 CONFIG_EXAMPLES_OSTEST=y
Task Control Interfaces
- task_create : 產生一個activates的新task,並回傳系統指派的pid
- task_init : 將task的TCB初始化,但並不activate task
- task_activate : activate task,否則scheduler沒辦法執行它
- task_delete : 將task關掉,並deallocate它的TCB與stack
- task_restart : 將task的children砍掉,deallocate TCB,reset priority
- task_exit : 關掉目前在運行的task
Task state
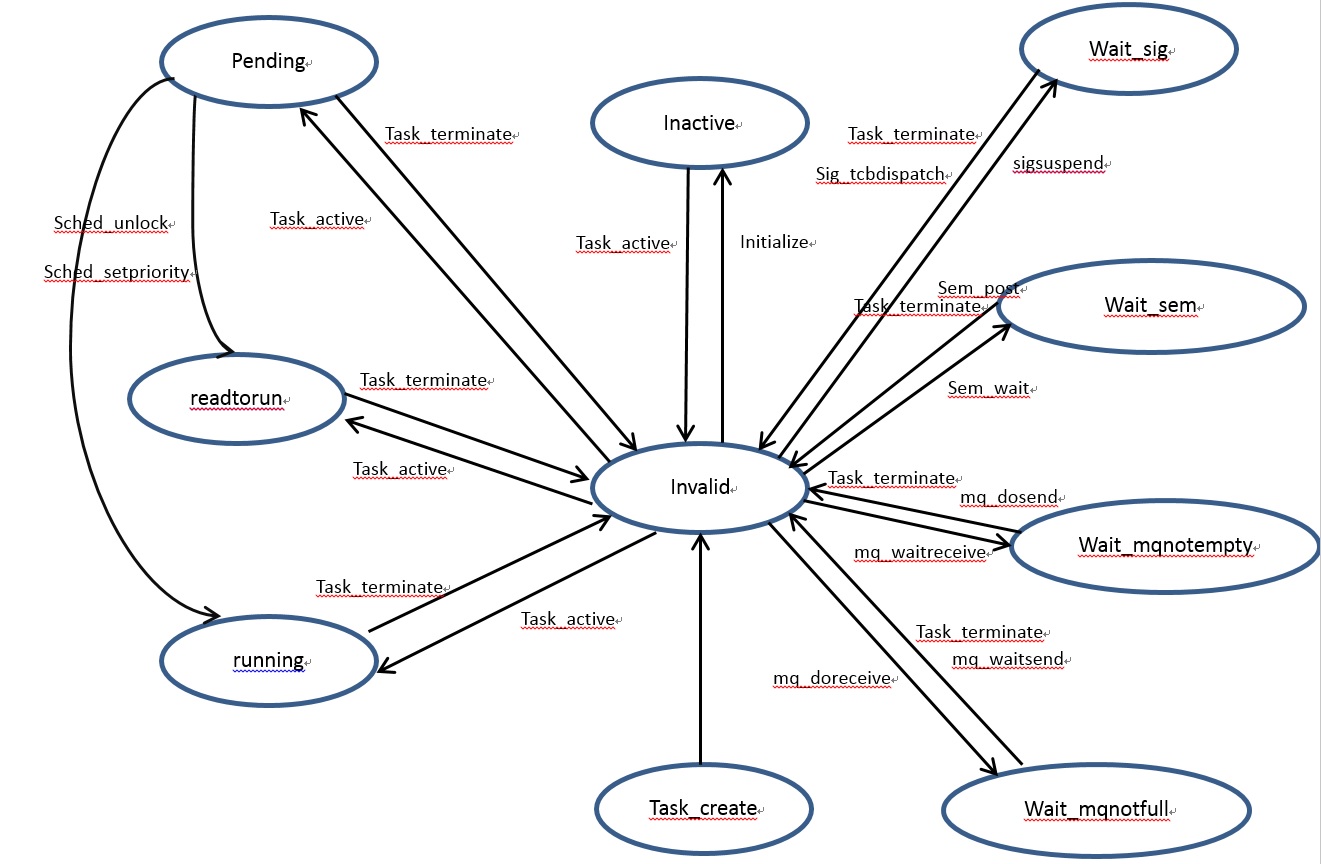
include/nuttx/sched.h
.. code-block:: c
enum tstate_e { TSTATE_TASK_INVALID = 0, /* INVALID - The TCB is uninitialized / TSTATE_TASK_PENDING, / READY_TO_RUN - Pending preemption unlock / TSTATE_TASK_READYTORUN, / READY-TO-RUN - But not running / TSTATE_TASK_RUNNING, / READY_TO_RUN - And running / TSTATE_TASK_INACTIVE, / BLOCKED - Initialized but not yet activated / TSTATE_WAIT_SEM, / BLOCKED - Waiting for a semaphore / #ifndef CONFIG_DISABLE_SIGNALS TSTATE_WAIT_SIG, / BLOCKED - Waiting for a signal / #endif #ifndef CONFIG_DISABLE_MQUEUE TSTATE_WAIT_MQNOTEMPTY, / BLOCKED - Waiting for a MQ to become not empty. / TSTATE_WAIT_MQNOTFULL, / BLOCKED - Waiting for a MQ to become not full. / #endif #ifdef CONFIG_PAGING TSTATE_WAIT_PAGEFILL, / BLOCKED - Waiting for page fill / #endif NUM_TASK_STATES / Must be last */ };
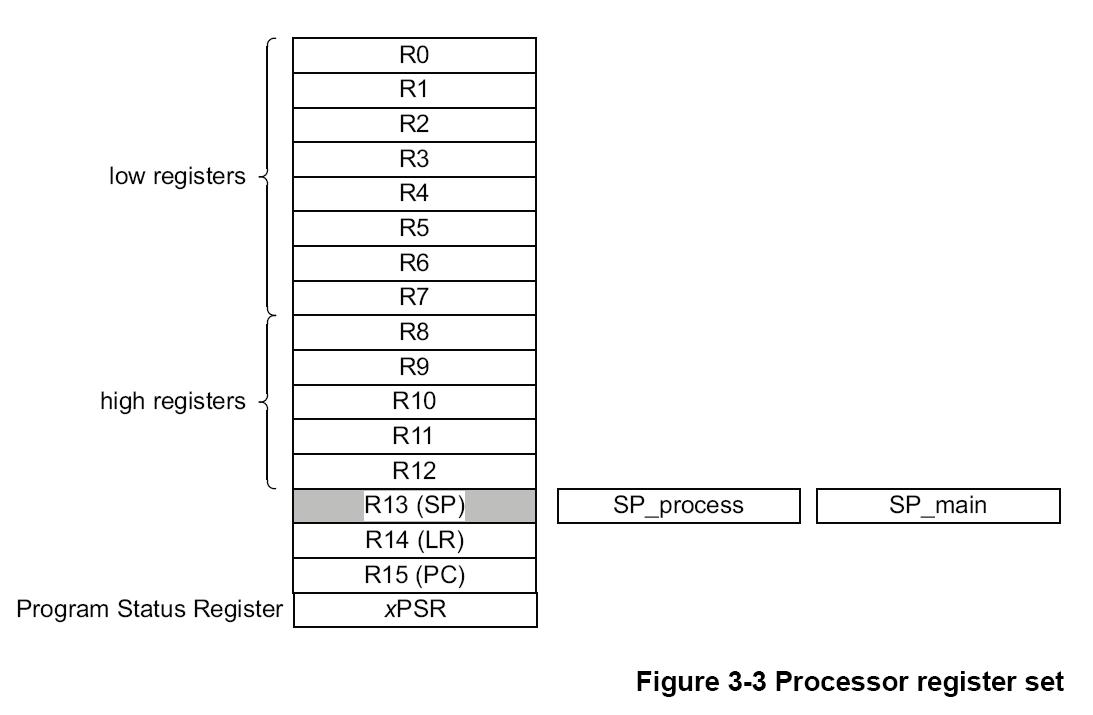
Register
Communication
| Semaphore | | sem_wait | sem_wait的主程式碼分為兩個部份,如果counter > 0,代表semaphore可以被hold,sem_wait會將task加入holder list | 否則sem_wait會block task,等待sem_hold unblock task,然後sem_wait再將task加入holder list .. code-block:: c
if (sem->semcount > 0) { sem->semcount–; sem_addholder(sem); rtcb->waitsem = NULL; ret = OK; }
else { sem->semcount–; rtcb->waitsem = sem; errno = 0; up_block_task(rtcb, TSTATE_WAIT_SEM);
if (errno != EINTR && errno != ETIMEDOUT) { sem_addholder(sem); ret = OK; } }
| sem_post | 一般而言,sem_post會在一個task要離開critical section的時候被呼叫 | 它會先呼叫sem_releaseholder,然後檢查counter是否<= 0,若是,代表還有task在等semaphore,sem_post會找到waiting list的下一個task,unblock它 .. code-block:: c
if (sem) { sem_releaseholder(sem); sem->semcount++; if (sem->semcount <= 0) { for (stcb = (FAR struct tcb_s*)g_waitingforsemaphore.head; (stcb && stcb->waitsem != sem); stcb = stcb->flink); if (stcb) { stcb->waitsem = NULL; up_unblock_task(stcb); } } }
| Mutex | nuttx的mutex實作是建立在semaphore上面 | 在使用mutex時,會先init一個binary semaphore,然後呼叫pthread_mutex_lock,pthread_mutex_lock會呼叫pthread_takesemaphore | pthread_takesemaphore會跑一個判別式是sem_wait的while loop | 當owner要交出使用權的時候,會呼叫pthread_mutex_unlock,pthread_mutex_unlock會將mutex->pid設成0,然後呼叫pthread_givesemaphore | pthread_givesemaphore會呼叫sem_post | | | pthread_mutexinit.c
.. code-block:: c
int pthread_mutex_init(FAR pthread_mutex_t mutex, FAR pthread_mutexattr_t attr) { : : status = sem_init((sem_t*)&mutex->sem, pshared, 1); : : }
| phread_mutexlock.c
.. code-block:: c
int pthread_mutex_lock(FAR pthread_mutex_t mutex) { : : : ret = pthread_takesemaphore((sem_t)&mutex->sem); if (!ret) { mutex->pid = mypid; } }
| pthread_initalize.c
.. code-block:: c
int pthread_takesemaphore(sem_t *sem) { if (sem) { while (sem_wait(sem) != OK) { : : : } return OK; }
}
.. code-block:: c
int pthread_givesemaphore(sem_t *sem) { if (sem) { if (sem_post(sem) == OK) { return OK; } else { set_errno(EINVAL); return ERROR; } } else { set_errno(EINVAL); return ERROR; } }
| pthread_mutexunlock.c
.. code-block:: c
int pthread_mutex_unlock(FAR pthread_mutex_t mutex) { : : :
{
{ mutex->pid = 0; : : : ret =
pthread_givesemaphore((sem_t)&mutex->sem); } sched_unlock();
} return ret; }
Scheduling
include/sys/types.h
.. code-block:: c
/* HPUX-like MIN/MAX value */
#define PRIOR_RR_MIN 0 #define PRIOR_RR_MAX 255 #define PRIOR_FIFO_MIN 0 #define PRIOR_FIFO_MAX 255 #define PRIOR_OTHER_MIN 0 /* Not use / #define PRIOR_OTHER_MAX 255 / Not use */
/* Scheduling Priorities. NOTE: Only the idle task can take * the true minimum priority. */
#define SCHED_PRIORITY_MAX 255 #define SCHED_PRIORITY_DEFAULT 100 #define SCHED_PRIORITY_MIN 1 #define SCHED_PRIORITY_IDLE 0
觀看每個設定time slice的相關檔案其運算是皆為 timeslice = CONFIG_RR_INTERVAL / MSEC_PER_TICK
在 nuttx/include/nuttx/config.h 中
CONFIG_RR_INTERVAL = 200
MSEC_PER_TICK = 10
此區禁止 context switch
sched_unlock()用在修改scheduler和priority。
此區暫停 timer interrupt
irqrestore(saved_state);
用在修改 scheduler。
注意:timer interrupt 跟 context switch 是不同系統。
Interrupt Handler
在nuttx/arch/arm/include/stm32/irq.h和nuttx/arch/arm/include/stm32/stm32f40xxx_irq.h中分別定義了可用的ISR name和對應的vector name
Processor Exceptions (vectors 0-15)
包括Internal和Software Interrupts,設定在nuttx/arch/arm/src/chip/stm32_irq.c:void up_irqinitialize(void)
.. code-block:: c
//nuttx/arch/arm/include/stm32/irq.h #define STM32_IRQ_RESERVED (0) /* Reserved vector (only used with CONFIG_DEBUG) / / Vector 0: Reset stack pointer value / / Vector 1: Reset (not handler as an IRQ) / #define STM32_IRQ_NMI (2) / Vector 2: Non-Maskable Interrupt (NMI) / #define STM32_IRQ_HARDFAULT (3) / Vector 3: Hard fault / #define STM32_IRQ_MEMFAULT (4) / Vector 4: Memory management (MPU) / #define STM32_IRQ_BUSFAULT (5) / Vector 5: Bus fault / #define STM32_IRQ_USAGEFAULT (6) / Vector 6: Usage fault / #define STM32_IRQ_SVCALL (11) / Vector 11: SVC call / #define STM32_IRQ_DBGMONITOR (12) / Vector 12: Debug Monitor / / Vector 13: Reserved / #define STM32_IRQ_PENDSV (14) / Vector 14: Pendable system service request / #define STM32_IRQ_SYSTICK (15) / Vector 15: System tick */
External interrupts (vectors >= 16)
外部中斷,設定在nuttx/arch/arm/src/stm32/chip/stm32f40xxx_vectors.h
.. code-block:: c
//nuttx/arch/arm/include/stm32/stm32f40xxx_irq.h #define STM32_IRQ_WWDG (STM32_IRQ_INTERRUPTS+0) /* 0: Window Watchdog interrupt / #define STM32_IRQ_PVD (STM32_IRQ_INTERRUPTS+1) / 1: PVD through EXTI Line detection interrupt / #define STM32_IRQ_TAMPER (STM32_IRQ_INTERRUPTS+2) / 2: Tamper and time stamp interrupts / #define STM32_IRQ_TIMESTAMP (STM32_IRQ_INTERRUPTS+2) / 2: Tamper and time stamp interrupts / #define STM32_IRQ_RTC_WKUP (STM32_IRQ_INTERRUPTS+3) / 3: RTC global interrupt / #define STM32_IRQ_FLASH (STM32_IRQ_INTERRUPTS+4) / 4: Flash global interrupt */ . . .
如何設定Interrupt Handler?
.. code-block:: c
//irq_attach(STM32_IRQ_SVCALL, up_svcall); //System Call
//nuttx/sched/irq_attach.c int irq_attach(int irq, xcpt_t isr) { state = irqsave(); //disables all interrupts if(isr == NULL) { up_disable_irq(irq); isr = irq_unexpected_isr; } g_irqvector[irq] = isr; //Vector Table irqrestore(state); ret = ok; }
Interrupt Handling的分層架構
low-level logic, arch/arm/src/armv7-m/up_exception.S, 接收Interrupt並決定IRQ number
That low-level logic than calls some MCU-specific, intermediate level function up_doirq(), mask and acknowledge the interrupt, dispatch, unmask
That MCU-specific function then calls the NuttX common interrupt dispatching logic irq_dispatch()
STM32_IRQ_SYSTICK
.. code-block:: c
//(void)irq_attach(STM32_IRQ_SYSTICK, (xcpt_t)up_timerisr); //up_exception.S -> up_doirq(int irq, uint32_t regs)-> irq_dispatch(int irq, FAR void context) -> up_timerisr(int irq, uint32_t *regs) -> sched_process_timer(void) -> sched_process_timeslice() static void sched_process_timeslice(void) { if((rtcb->flags & TCB_FLAG_ROUND_ROBIN) != 0) { if(rtcb->timeslice <= 1) { if(!rtcb->lockcount) { rtcb->timeslice = CONFIG_RR_INTERVAL/MSEC_PER_TICK; if (rtcb->flink && rtcb->flink->sched_priority >= rtcb->sched_priority) { up_reprioritize_rtr(rtcb, rtcb->sched_priority); } } } else { rtcb->timeslice–; } } }
Configuring High Priority Interrupts
How do you specify a high priority interrupt? if CONFIG_ARCH_RAMVECTORS=y, then vectors will be kept in RAM and the system will support the interface
int up_ramvec_attach(int irq, up_vector_t vector). That interface can be used to attach your C interrupt handler to the vector at run time.
.. code-block:: c
//up_vector_t g_ram_vectors[ARMV7M_VECTAB_SIZE] attribute((section(“.ram_vectors”))); //Using a RAM-based vector table //void up_ramvec_initialize(void) //Copy vectors to RAM an configure the NVIC to use the RAM vectors. int up_ramvec_attach(int irq, up_vector_t vector) //Configure the ram vector table so that IRQ number ‘irq’ will be dipatched by hardware to ‘vector’ { int ret = ERROR; if ((unsigned)irq < ARMV7M_PERIPHERAL_INTERRUPTS) { irqstate_t flags; flags = irqsave(); if (vector == NULL) { up_disable_irq(irq); vector = exception_common; } g_ram_vectors[irq] = vector; irqrestore(flags); ret = OK; } return ret; }
FPU
儲存 fpu 的 context switch
.. code-block:: c
up_savefpu:
add r1, r0, #(4REG_S0) / R1=Address of FP register storage */
/* Some older GNU assemblers don’t support all the newer UAL mnemonics. */
#if 1 /* Use UAL mnemonics / / Store all floating point registers. Registers are stored in numeric order, * s0, s1, … in increasing address order. */
vstmia r1!, {s0-s31} /* Save the full FP context */
/* Store the floating point control and status register. At the end of the * vstmia, r1 will point to the FPCSR storage location. */
vmrs r2, fpscr /* Fetch the FPCSR / str r2, [r1], #4 / Save the floating point control and status register / #else / Store all floating point registers */
#if 1 /* Use store multiple / fstmias r1!, {s0-s31} / Save the full FP context / #else vmov r2, r3, d0 / r2, r3 = d0 / str r2, [r1], #4 / Save S0 and S1 values / str r3, [r1], #4 vmov r2, r3, d1 / r2, r3 = d1 / str r2, [r1], #4 / Save S2 and S3 values / str r3, [r1], #4 vmov r2, r3, d2 / r2, r3 = d2 / str r2, [r1], #4 / Save S4 and S5 values / str r3, [r1], #4 vmov r2, r3, d3 / r2, r3 = d3 / str r2, [r1], #4 / Save S6 and S7 values / str r3, [r1], #4 vmov r2, r3, d4 / r2, r3 = d4 / str r2, [r1], #4 / Save S8 and S9 values / str r3, [r1], #4 vmov r2, r3, d5 / r2, r3 = d5 / str r2, [r1], #4 / Save S10 and S11 values / str r3, [r1], #4 vmov r2, r3, d6 / r2, r3 = d6 / str r2, [r1], #4 / Save S12 and S13 values / str r3, [r1], #4 vmov r2, r3, d7 / r2, r3 = d7 / str r2, [r1], #4 / Save S14 and S15 values / str r3, [r1], #4 vmov r2, r3, d8 / r2, r3 = d8 / str r2, [r1], #4 / Save S16 and S17 values / str r3, [r1], #4 vmov r2, r3, d9 / r2, r3 = d9 / str r2, [r1], #4 / Save S18 and S19 values / str r3, [r1], #4 vmov r2, r3, d10 / r2, r3 = d10 / str r2, [r1], #4 / Save S20 and S21 values / str r3, [r1], #4 vmov r2, r3, d11 / r2, r3 = d11 / str r2, [r1], #4 / Save S22 and S23 values / str r3, [r1], #4 vmov r2, r3, d12 / r2, r3 = d12 / str r2, [r1], #4 / Save S24 and S25 values / str r3, [r1], #4 vmov r2, r3, d13 / r2, r3 = d13 / str r2, [r1], #4 / Save S26 and S27 values / str r3, [r1], #4 vmov r2, r3, d14 / r2, r3 = d14 / str r2, [r1], #4 / Save S28 and S29 values / str r3, [r1], #4 vmov r2, r3, d15 / r2, r3 = d15 / str r2, [r1], #4 / Save S30 and S31 values */ str r3, [r1], #4 #endif
/* Store the floating point control and status register */
fmrx r2, fpscr /* Fetch the FPCSR / str r2, [r1], #4 / Save the floating point control and status register */ #endif bx lr
.size up_savefpu, .-up_savefpu
.. code-block:: c
up_restorefpu:
add r1, r0, #(4REG_S0) / R1=Address of FP register storage */
/* Some older GNU assemblers don’t support all the newer UAL mnemonics. */
#if 1 /* Use UAL mnemonics / / Load all floating point registers. Registers are loaded in numeric order, * s0, s1, … in increasing address order. */
vldmia r1!, {s0-s31} /* Restore the full FP context */
/* Load the floating point control and status register. At the end of the * vstmia, r1 will point to the FPCSR storage location. */
ldr r2, [r1], #4 /* Fetch the floating point control and status register / vmsr fpscr, r2 / Restore the FPCSR / #else / Load all floating point registers Registers are loaded in numeric order, * s0, s1, … in increasing address order. */
#if 1 /* Use load multiple / fldmias r1!, {s0-s31} / Restore the full FP context / #else ldr r2, [r1], #4 / Fetch S0 and S1 values / ldr r3, [r1], #4 vmov d0, r2, r3 / Save as d0 / ldr r2, [r1], #4 / Fetch S2 and S3 values / ldr r3, [r1], #4 vmov d1, r2, r3 / Save as d1 / ldr r2, [r1], #4 / Fetch S4 and S5 values / ldr r3, [r1], #4 vmov d2, r2, r3 / Save as d2 / ldr r2, [r1], #4 / Fetch S6 and S7 values / ldr r3, [r1], #4 vmov d3, r2, r3 / Save as d3 / ldr r2, [r1], #4 / Fetch S8 and S9 values / ldr r3, [r1], #4 vmov d4, r2, r3 / Save as d4 / ldr r2, [r1], #4 / Fetch S10 and S11 values / ldr r3, [r1], #4 vmov d5, r2, r3 / Save as d5 / ldr r2, [r1], #4 / Fetch S12 and S13 values / ldr r3, [r1], #4 vmov d6, r2, r3 / Save as d6 / ldr r2, [r1], #4 / Fetch S14 and S15 values / ldr r3, [r1], #4 vmov d7, r2, r3 / Save as d7 / ldr r2, [r1], #4 / Fetch S16 and S17 values / ldr r3, [r1], #4 vmov d8, r2, r3 / Save as d8 / ldr r2, [r1], #4 / Fetch S18 and S19 values / ldr r3, [r1], #4 vmov d9, r2, r3 / Save as d9 / ldr r2, [r1], #4 / Fetch S20 and S21 values / ldr r3, [r1], #4 vmov d10, r2, r3 / Save as d10 / ldr r2, [r1], #4 / Fetch S22 and S23 values / ldr r3, [r1], #4 vmov d11, r2, r3 / Save as d11 / ldr r2, [r1], #4 / Fetch S24 and S25 values / ldr r3, [r1], #4 vmov d12, r2, r3 / Save as d12 / ldr r2, [r1], #4 / Fetch S26 and S27 values / ldr r3, [r1], #4 vmov d13, r2, r3 / Save as d13 / ldr r2, [r1], #4 / Fetch S28 and S29 values / ldr r3, [r1], #4 vmov d14, r2, r3 / Save as d14 / ldr r2, [r1], #4 / Fetch S30 and S31 values / ldr r3, [r1], #4 vmov d15, r2, r3 / Save as d15 */ #endif
/* Load the floating point control and status register. r1 points t * the address of the FPCSR register. */
ldr r2, [r1], #4 /* Fetch the floating point control and status register / fmxr fpscr, r2 / Restore the FPCSR */ #endif bx lr
.size up_restorefpu, .-up_restorefpu #endif /* CONFIG_ARCH_FPU */
struct xcptcontext
/nuttx/arch/arm/include/armv7-m/irq_lazyfpu.h
XCPTCONTEXT_REGS = HW_XCPT_REGS + SW_XCPT_REGS
XCPTCONTEXT_SIZE = 4 * XCPTCONTEXT_REGS
其中8個為硬體一般暫存器包含R0 to R3, R12, R14 = LR, R15 = PC, XPSR
其中軟體暫存器浮點數FP共33個 S0 to S31, FPSCR
原本10個軟體一般暫存器 R13 = SP, PRIMASK, R4 to R11
依序存入XCPT由software registers SP開始到R11,浮點數S0到FPSCR,再來是 hardware registers R0到XPSR
測試環境架設
硬體驅動原理
- UART
- FPU (Floating Point Unit)
效能表現
參考資料
- https://github.com/deadbeefcafe/nuttx-stm32f4disc-bb
- http://bibliodigital.itcr.ac.cr/xmlui/bitstream/handle/2238/3051/FinalReport.pdf
